Taxes can feel confusing when you’re just starting to manage your own money. You might wonder why your salary changes after deductions or how people save so much through smart tax moves. If you’ve ever asked yourself whether you’re handling your taxes the right way, you’re not alone.
Understanding the basics early helps you protect your income, avoid penalties, and make better financial decisions. It also makes concepts like tax management in income tax easier to handle, especially when you're juggling rent or bills. Good tax habits today can save you both time and stress later.
In this blog, we’ll break down tax planning, tax management, the differences between them, smart saving options, and how all of this fits into your financial journey. Let’s make tax season simpler, clearer, and far less intimidating.
Key Takeaways:
- Tax planning helps reduce your tax liability legally through smart investments and available deductions.
- Tax management focuses on timely filings, proper records, and continuous compliance throughout the year.
- Young earners benefit from early tax filing, clean records, and timely deductions to avoid penalties.
- Popular tax-saving options include ELSS, PPF, life insurance, and health insurance premiums.
- Good documentation, timely returns, and advance tax payments form the core of effective tax management.
What Is Tax Planning And Its Key Components?
When you start earning, taxes can feel confusing, but tax planning makes things easier. Simply put, tax planning is a way to strategically structure your income, investments, and expenses so you pay only what you should, not more than that.
Key Components of Tax Planning
- Proactive approach: Plan before tax liabilities arise, not after.
- Legal methods: Use deductions under sections like 80C to 80U, or exemptions on house rent and home loan interest.
- Short-term and long-term strategies: Short-term for immediate benefits, long-term for multi-year savings.
- Financial integration: Align your tax planning with investments, insurance, and loan decisions.
Tax planning doesn’t mean hiding income or avoiding tax. It is a legal and sensible way of arranging your money so you stay on top of your finances.
As you explore this stage, you might wonder what happens after you plan. This is where tax management comes in, and it plays a very different role.
What Is Tax Management And Its Key Components?
If tax planning helps you save money, tax management helps you stay compliant. It is the day-to-day handling of tax rules so you avoid late fees, mistakes and penalties. You’ll often hear the term tax management in income tax, because it covers everything from keeping records to filing your return on time.
Key Components of Tax Management
- Compliance focus: File returns, pay taxes, and respond to notices on time.
- Record-keeping: Maintain salary slips, bank statements, TDS certificates, and investment proofs.
- Risk management: Identify audit triggers and keep documentation ready for authorities.
- Continuous process: Unlike tax planning, which happens periodically, tax management is year-round.
Unlike tax planning, tax management is compulsory for every taxpayer. Even if you don’t claim many deductions, you still need to follow timelines and keep your documents ready.
With the basics of both concepts clear, let's look at why these practices matter at all.
Why Tax Planning And Management Matter?
Ever wondered why people stress about taxes every year? The truth is, good tax practices can make a big difference in your financial life. Whether you’re planning to switch jobs, start freelancing or take your first loan, smart tax planning and management give you a strong base.
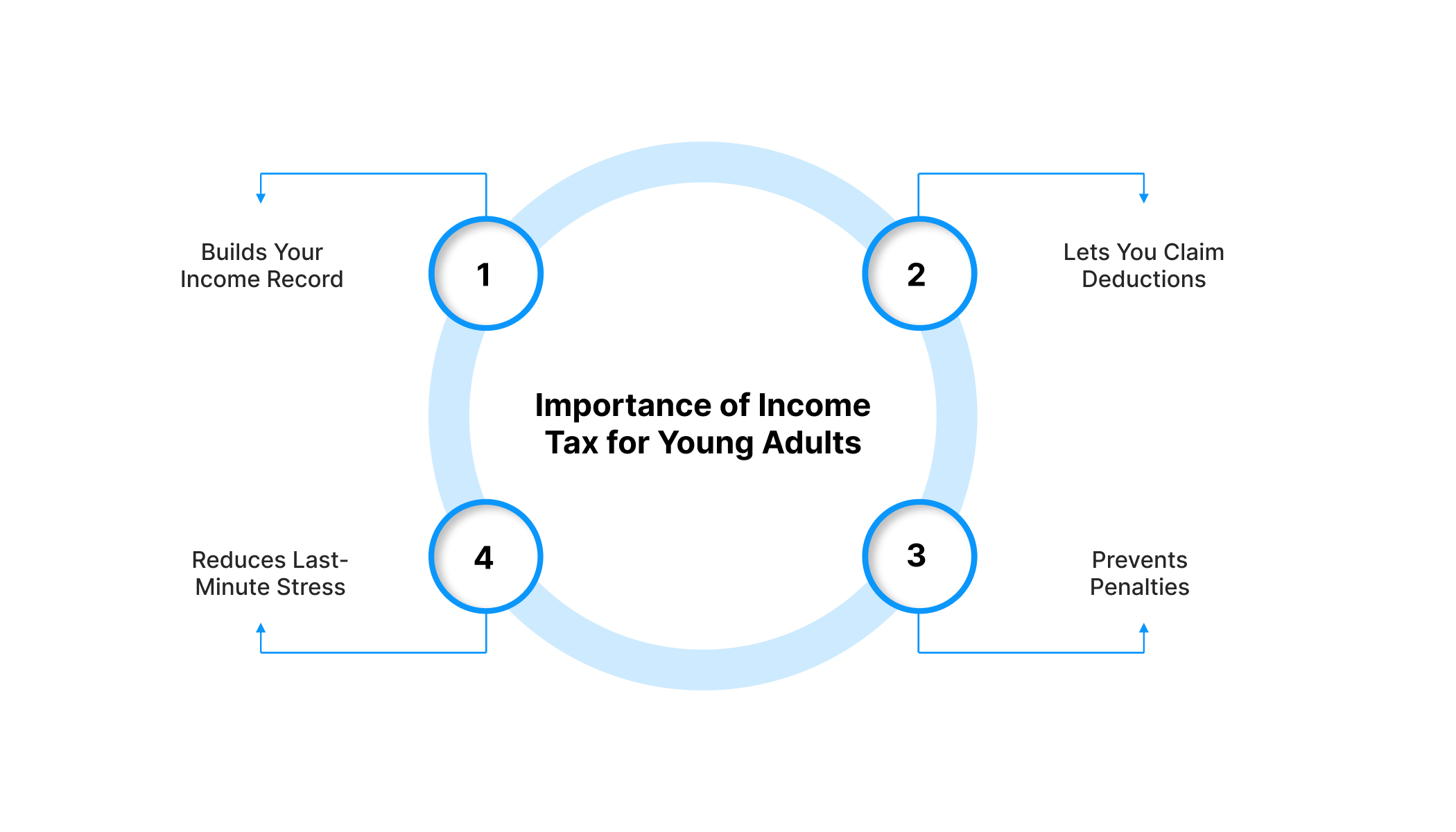
Importance of Income Tax for Young Adults
Income tax isn’t just a payment you make once a year. It connects to many parts of your financial life, especially when you’re managing expenses on a tight budget. Here are a few reasons it matters:
- Builds Your Income Record: Filing your taxes regularly builds a clear income history, which banks often check before offering credit.
- Lets You Claim Deductions: You can claim deductions for investments, insurance, and education expenses, reducing your tax outflow.
- Prevents Penalties: Staying compliant protects you from late fees, interest charges, or unwanted legal trouble.
- Reduces Last-Minute Stress: Filing early helps you avoid rushed decisions and last-minute mistakes during the tax season.
Example: If you are investing in an ELSS mutual fund, you can save taxes under Section 80C while growing wealth for the future. Similarly, keeping all TDS certificates and filing returns on time ensures you avoid penalties and maintain a clean tax record.
Now that you know why taxes matter, it’s time to look at how planning and management stand apart from each other.
Also Read: Basic Salary Calculation: Factors, Deductions and Tax Liability
Tax Planning vs Tax Management: Key Differences
You’ve seen what tax planning and tax management mean on their own. Now, you might be curious about how they actually differ when you look at them side by side.
Here’s a simple comparison so you can see how both support your financial life:
| Area | Tax Planning | Tax Management |
| Purpose | Reduce tax legally through smart choices | Follow tax rules and stay compliant |
| Timing | Mostly before financial decisions | Ongoing through the year |
| Approach | Strategic and goal-based | Practical and process-focused |
| Activity | Selecting investments, claiming deductions | Filing returns, storing documents, paying dues |
| Requirement | Optional but useful | Mandatory for all taxpayers |
| Outcome | Lower tax outflow | Fewer penalties and smoother paperwork |
Both are important, but they work in different ways. Tax planning helps you reduce what you owe, while tax management keeps your tax responsibilities organised. When this becomes clear, choosing the right tax-saving options gets much easier.
Popular Tax-Saving Options For Young Indians
If you’ve ever wondered where to start with tax-saving, know that India offers several provisions under the Income Tax Act. Knowing your options early helps you save more and build better financial habits.
Section 80C: Investment-Based Savings
Section 80C allows you to get a claim of up to ₹1.5 lakh each financial year. Young earners can often use these three choices:
- ELSS Funds: These market-linked funds have a three-year lock-in and higher growth potential. They suit beginners who want both tax savings and wealth creation.
- PPF: This long-term savings plan offers steady returns and tax-free maturity. It’s ideal if you prefer safer investments.
- Life Insurance Premiums: Premiums qualify for deductions, and some policies also provide additional tax perks depending on their structure.
Section 80D: Health Cover
Health insurance premiums for yourself, your family or your parents can reduce your taxable income. This helps manage medical expenses while saving on taxes.
- Deduction of up to ₹25,000 for self and family
- Additional deduction for parents’ insurance based on their age
Other Helpful Options
Here are a few more choices that young taxpayers can consider:
- Contributions to NPS for long-term retirement savings
- Tuition fee deductions for dependent children
- Donations to approved charitable organisations
Each option works differently, so choosing a mix that suits your goals is usually the best approach. Once you figure that out, the next step is managing your taxes well throughout the year.
Also Read: Top Tax Saving Tips for Salaried Individuals
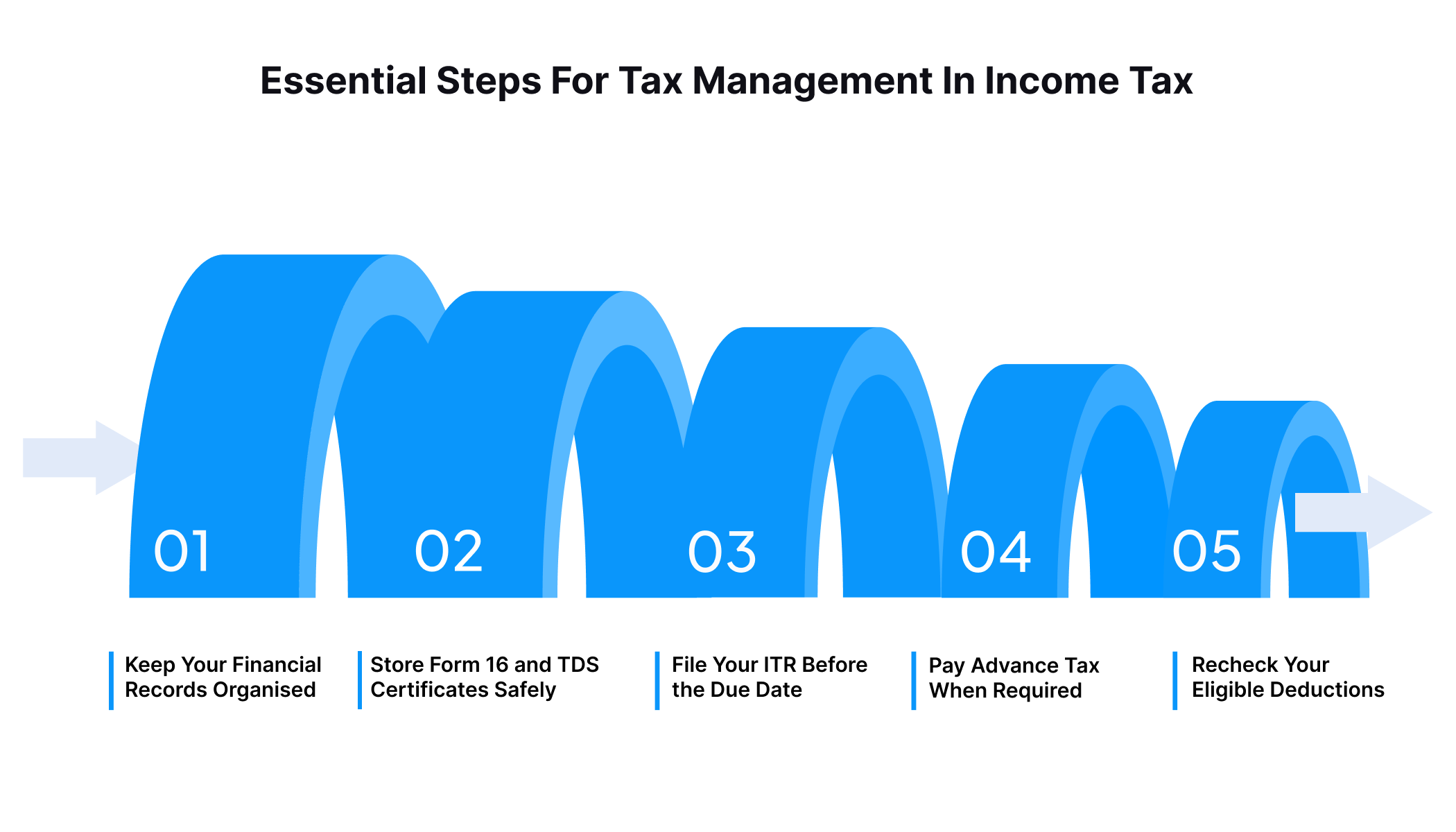
Essential Steps For Tax Management In Income Tax
You’ve seen the saving part, but staying compliant is equally important. Effective tax management in income tax is about keeping things simple, timely, and well-documented. These essentials help you avoid penalties and stay confident during tax filings.
Here’s what you can follow:
- Keep Your Financial Records Organised
Keep salary slips, rent proofs, bank statements, and investment documents in one place. This helps you file accurately and avoids rushing to find documents at the last moment.
- Store Form 16 and TDS Certificates Safely
Form 16 and TDS certificates confirm the tax already deducted from your income. Keeping them handy ensures the details in your return match your employer’s records.
- File Your ITR Before the Due Date
The typical deadline for filing your income tax return is 31 July each year. Filing on time helps you avoid penalties and keeps your financial history clean.
- Pay Advance Tax When Required
If your tax liability exceeds ₹10,000 after TDS, you must pay advance tax in instalments. Doing this on schedule prevents interest charges and last-minute stress.
- Recheck Your Eligible Deductions
Review your deductions from time to time so you don’t miss out on savings. A quick check can help you claim everything you qualify for under the law.
These steps help you stay compliant and avoid unnecessary stress, especially as your income grows. And when your taxes are in order, it becomes easier to access financial products.
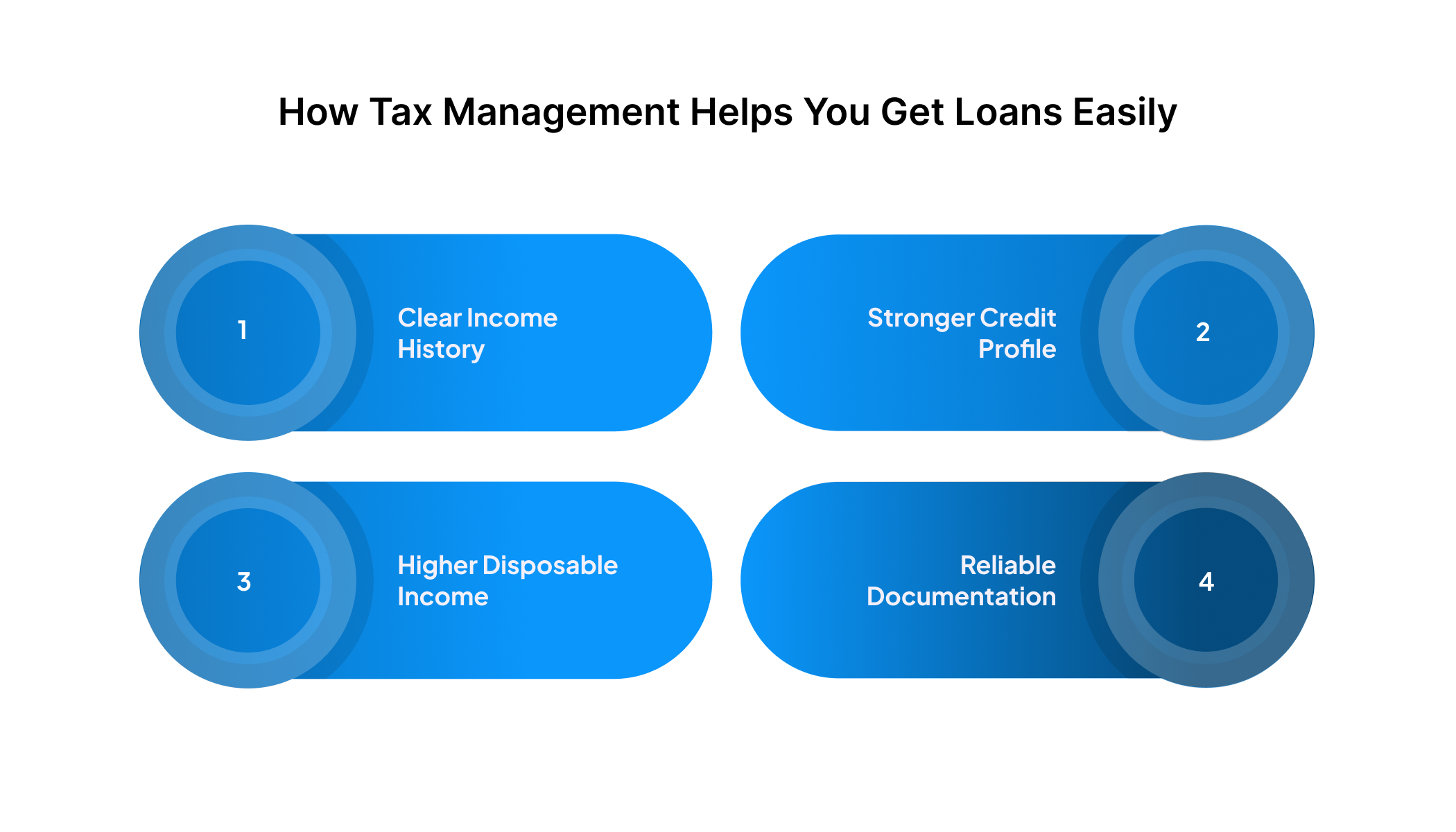
How Tax Management Helps You Get Loans Easily
When you apply for a loan, lenders look beyond your salary. They check your financial behaviour, including how responsible you are with taxes. Good tax management creates a solid financial record, making you a more reliable borrower.
Here’s how it helps:
- Clear Income History: Regular tax filing creates a verified income trail, helping lenders accurately assess your earning stability during loan evaluations.
- Stronger Credit Profile: Consistent tax compliance signals financial reliability to lenders, improving your overall creditworthiness for future borrowing.
- Higher Disposable Income: Smart tax-saving increases take-home income. This strengthens your repayment ability and supports smoother EMI planning.
- Reliable Documentation: Well-maintained tax records simplify lender verification processes, speeding up approvals and reducing documentation issues.
Young borrowers often overlook how important tax discipline is. But when you keep your taxes sorted, getting financial support, whether for emergencies or planned expenses, becomes much smoother.
Also Read: Understanding TAN and Its Application
How Pocketly Helps You Handle Sudden Expenses During Tax Season
Tax season often brings unexpected payments or tight cash flow, especially when you're managing bills, savings, or new responsibilities. If you ever face a short-term crunch, Pocketly offers a practical way to steady your budget without stress.
Pocketly is a digital lending platform (not an NBFC) that provides short-term, collateral-free personal loans ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000. The interest rate starts at 2% per month, with a processing fee of 1-8% of the loan amount. The entire process is simple and online, with simple KYC, no collateral, and fast approval.
How it works:
- Sign up using your mobile number.
- Upload PAN, Aadhaar and complete quick KYC.
- Enter your bank details for secure transfers.
- Select your loan amount and repayment tenure.
- Get the money transferred to your account within minutes.
With 24/7 support and a hassle-free experience, Pocketly helps you handle urgent costs without slipping behind on your tax responsibilities.
Wrapping Up
Understanding the difference between tax planning and tax management helps you stay organised, reduce your tax burden, and avoid last-minute stress. When you know how tax management in income tax works, you get more control over your savings and spending. The earlier you build good habits, the stronger your financial base becomes.
As you continue learning and taking control of your money, remember that some months can still bring sudden expenses or tight cash flow, especially around tax deadlines. That’s when having a simple and dependable short-term solution can make a real difference.
If you ever need quick help during those moments, Pocketly can help. Download Pocketly on iOS or Android and keep a dependable option ready for unexpected needs.
FAQ’s
How to avoid 40% tax?
You can reduce your tax burden by using deductions like 80C, 80D and interest-related tax benefits. Planning investments early in the year helps prevent your income from entering higher tax brackets.
Is tax management legal or illegal?
Tax management is completely legal because it focuses on compliance, timely filing, and proper documentation. It becomes illegal only when someone hides income or intentionally provides false information.
How to properly record income tax paid electronically?
Save digital copies of challans, bank receipts, and your Form 26AS as proof of payment. Match these records with the entries on the income tax portal to ensure accuracy.
Who pays 30% tax in India?
Under the old tax regime, individuals earning income in the highest slab fall into the 30% bracket. This rate does not automatically apply under the new regime, where slab structures differ.
Which type of tax is GST?
GST is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India. It replaces multiple older taxes like VAT, excise duty, and service tax.