Filing your income tax return can be a stressful process, especially when your return gets flagged by the Income Tax Department's risk management system. Whether it’s due to mismatched data, incorrect deductions, or unusually high refund claims, seeing a warning about your return can cause anxiety and confusion.
The last thing you want is to have your refund delayed, or worse, your return marked as invalid. Such issues can disrupt your financial planning and leave you scrambling to fix mistakes at the last minute. What makes matters worse is the complexity of responding to such alerts; you may not even know where to start.
But don’t worry, understanding the risk management process can put your mind at ease. In this blog, we’ll break down how the system works, what triggers a flag, and how you can quickly and effectively respond to ensure your return is processed smoothly and without delays.
TL;DR
- The Income Tax Department uses an automated risk management system to flag returns with mismatches, unusual deductions, or high refund claims.
- Being flagged doesn’t mean wrongdoing; it simply means your return needs verification against data like Form 26AS and AIS.
- Common triggers include income mismatches, overstated deductions, incorrect capital gains, undeclared foreign assets, and large cash transactions.
- You can resolve most alerts by reviewing your return, submitting clarifications or documents, or filing a revised/rectified return within the given timeframe.
- Responding promptly and accurately helps avoid refund delays, penalties, and future scrutiny while keeping your tax filing stress-free.
What Is the Risk Management Process in Income Tax?
The risk management process in income tax is a mechanism used by the Income Tax Department to assess, identify, and manage risks associated with tax filings. This process is designed to ensure that all income tax returns (ITRs) are accurate and compliant with the law. It uses advanced analytics and data comparison techniques to flag returns that may contain discrepancies or unusual claims that warrant further scrutiny.
Instead of reviewing every tax return manually, the department relies on automated systems to analyse returns and compare them with third-party data such as TDS (Tax Deducted at Source), AIS (Annual Information Statement), and other government records. If the system detects a mismatch or something unusual, the return is flagged for further review.
While being flagged doesn't necessarily indicate wrongdoing, it does mean the department wants to ensure the accuracy of your submission. Understanding how this process works can help you avoid common mistakes and ensure that your return is processed smoothly.
How does the Risk Management Process Work?
The risk management process for income tax filing is a strategic system used by the Income Tax Department to ensure that all returns are legitimate, accurate, and compliant. This process uses automation, data analytics, and predefined algorithms to identify potential discrepancies and reduce the risk of fraud.
Here’s a deeper look into how the risk management system works and the steps involved:
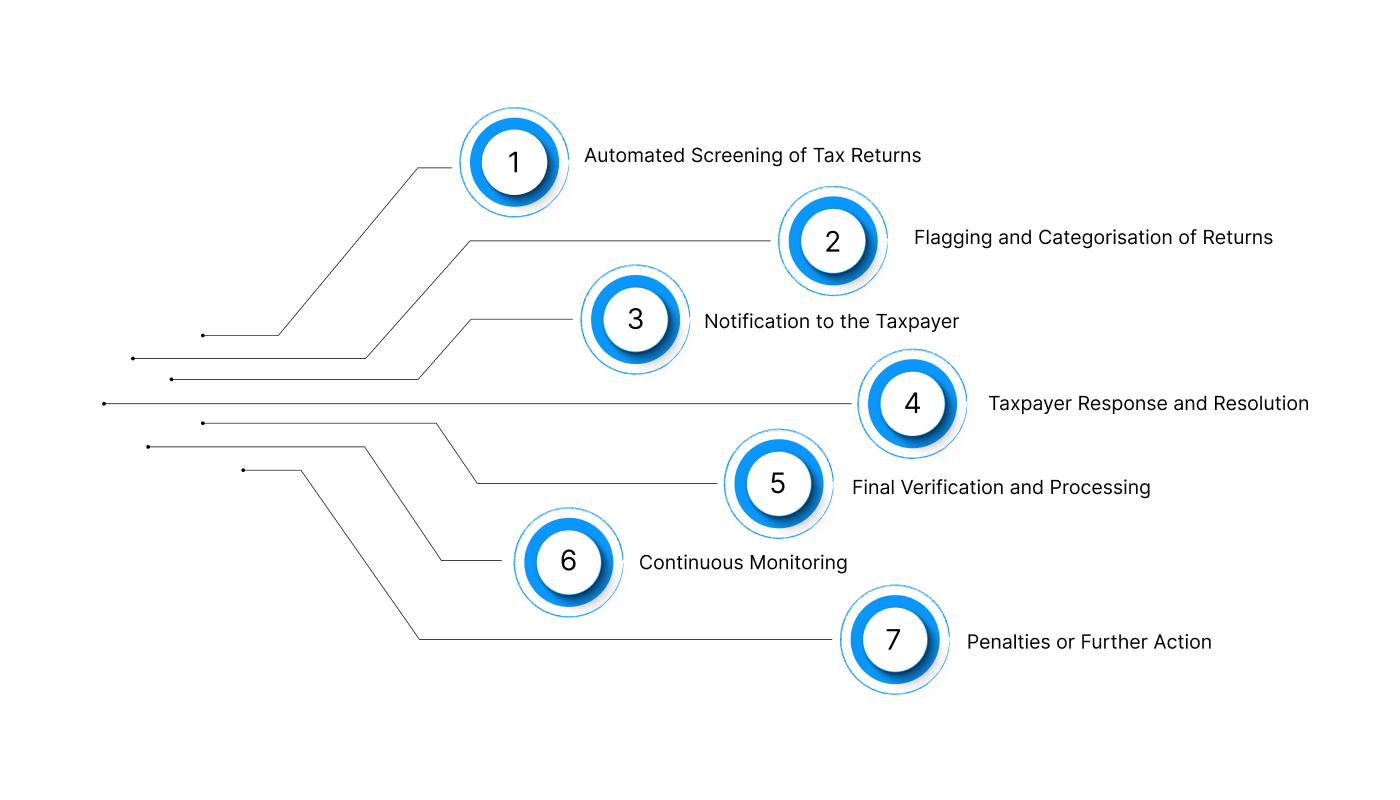
1. Automated Screening of Tax Returns
The first step in the process involves the automated screening of returns. Using sophisticated technology, the Income Tax Department analyses the data provided by taxpayers. This step compares return details with several external sources, including:
- Form 26AS (Tax Credit Statement)
- Annual Information Statement (AIS)
- Data from third parties like banks, employers, and mutual funds
This helps identify inconsistencies, such as mismatches between reported income and third-party data, unusual claims, or irregularities in tax paid. The system also looks for incomplete or erroneous information.
2. Flagging and Categorisation of Returns
Once a return is screened, the system flags any anomalies or outliers. These flagged returns are categorised into different risk levels depending on the severity and type of the discrepancy. Returns with minor issues might be flagged for clarification, while more serious discrepancies could trigger a deeper investigation.
Types of discrepancies that may be flagged include:
- Mismatch of income: If the reported income doesn’t match what is reported by employers or banks.
- Excessive deductions: When claimed deductions exceed reasonable limits or don’t have proper supporting evidence.
- Large refund claims: Excessive refund claims compared to the tax paid in previous years.
3. Notification to the Taxpayer
Once the return is flagged, the Income Tax Department notifies the taxpayer through various channels:
- Email/SMS notifications
- Alerts on the Income Tax e-filing portal
The notification may ask the taxpayer to:
- Verify or correct information
- Submit additional documents
- Clarify inconsistencies in reported data (e.g., mismatched income or deductions)
4. Taxpayer Response and Resolution
After receiving the notification, the taxpayer is given the opportunity to respond to the notice or revise the return if discrepancies are identified. The taxpayer may either:
- Submit clarification or documentation to prove the legitimacy of the claims made in the return.
- File a revised return if errors were made in the original submission.
The Income Tax Department typically provides clear guidelines on how to correct errors, and in most cases, this can be done without facing penalties as long as the response is timely and the information is accurate.
5. Final Verification and Processing
After the taxpayer responds or submits a revised return, the Income Tax Department reviews the additional information. If everything checks out, the return is processed, and the refund or assessment is finalised. If the issues are unresolved, the return may be subject to further scrutiny or audit procedures.
- Refund Issuance: If no further issues are found, the refund is processed.
- Audit: If discrepancies remain, the return is flagged for a deeper audit or investigation.
6. Continuous Monitoring
The risk management system does not end with a one-time screening. Returns flagged during this process may be subject to ongoing monitoring. This is to ensure that taxpayers continue to comply with tax laws and to catch any issues that may arise in future filings.
If a taxpayer is consistently flagged for discrepancies in multiple years, their return might face more frequent scrutiny or audit investigations in the future.
7. Penalties or Further Action
If the Income Tax Department identifies deliberate fraud or substantial misreporting after reviewing the flagged return, they may take further action:
- Penalties: Financial penalties for under-reporting or incorrect filing.
- Prosecution: Legal action could be taken if tax evasion is suspected.
- Interest on Tax Due: If the discrepancies result in underpayment, interest may be charged.
The risk management system plays a crucial role in ensuring that only legitimate returns are processed, minimising the risk of tax fraud or incorrect refunds.
Also Read: Top Tax Saving Tips for Salaried Individuals
Common Risks in the Income Tax Filing Process and How to Mitigate Them
While the Income Tax Department’s risk management system helps identify issues in tax returns, taxpayers also need to be aware of common risks that can trigger alerts or audits. By understanding these risks, you can take steps to mitigate them and ensure the smooth processing of your tax return.
Here’s a breakdown of some typical risks in the filing process and how to manage them effectively:
1. Mismatch in Reported Income
Risk: Reporting income that doesn’t match the details submitted by employers, banks, or other third parties can raise flags with the Income Tax Department. This is commonly seen when:
- The TDS shown in Form 26AS doesn’t match the reported income.
- There are discrepancies in salary details or bank interest income.
Mitigation:
- Ensure accuracy: Double-check your Form 26AS and cross-reference it with the income you report.
- Report all income sources: Include all income, such as interest from savings, salary, freelance work, and investments.
- Rectify discrepancies: If there’s a mismatch, update your return or submit a rectification request promptly.
2. Overstated Deductions
Risk: Claiming deductions that exceed the permissible limits or not having sufficient documentation to support them can lead to the flagging of returns. Common issues include:
- Claiming excessive deductions under Section 80C (life insurance premiums, PPF, etc.) without proper receipts.
- Incorrectly claiming home loan interest deductions or medical expenses that don’t align with actual payments.
Mitigation:
- Be precise with deductions: Only claim what you are eligible for and ensure you have supporting documents like receipts, invoices, and bank statements.
- Keep records: Maintain all receipts and proof of your investments or expenses for at least 5 years in case the tax department requests them.
3. Large Refund Claims
Risk: Submitting a return that claims a large refund relative to your income or previous years’ filings can raise suspicion. This is particularly risky if the refund is significantly higher than your tax liability.
Mitigation:
- Verify refund claims: Make sure your refund claim is accurate, based on proper calculations of taxes paid or TDS deducted.
- Check the filing status: Ensure that all information regarding income and tax payments is correctly reported.
4. Failure to Declare Foreign Assets or Income
Risk: Not reporting foreign income or assets, including bank accounts, investments, or properties abroad, can trigger audits or penalties, especially with increasing international tax compliance rules.
Mitigation:
- Disclose all foreign income and assets: If applicable, report all foreign earnings, assets, or investments as required under the Black Money Act and FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act).
- File the correct schedules: Use the Schedule FA to report foreign assets and income correctly.
5. Incorrectly Reported Capital Gains
Risk: Inaccurately reporting capital gains from the sale of assets like property, stocks, or mutual funds can lead to scrutiny. Taxpayers may either understate their gains or fail to consider capital loss adjustments.
Mitigation:
- Accurate calculations: Ensure correct calculation of short-term and long-term capital gains and report them based on your tax bracket.
- Keep records of transactions: Retain records of the sale/purchase date, amount, and related costs for your capital assets.
6. Unexplained Cash Transactions
Risk: Large, unexplained cash transactions or deposits that don’t align with the reported income can trigger investigations.
Mitigation:
- Avoid large cash deposits: Keep records of all cash transactions, and avoid large cash deposits without corresponding income sources.
- Report substantial cash transactions: If you engage in large cash transactions, especially those above ₹2,00,000, ensure these are reported and explained properly.
7. Use of Incorrect or Fraudulent Documents
Risk: Submitting fraudulent or altered documents can result in severe penalties or legal action. Using fake invoices, receipts, or misrepresenting information can trigger audits and investigations.
Mitigation:
- Use genuine documents: Only submit authentic and accurate documents. Never attempt to alter or falsify any paperwork.
- Double-check all claims: If any information is unclear or incorrect, rectify it before submission to avoid complications later.
Also Read: Understanding TAN and Its Application
How to Respond to Income Tax Risk Management Alerts
If your income tax return is flagged by the Risk Management System, here’s a structured way to respond and ensure your return is processed smoothly:
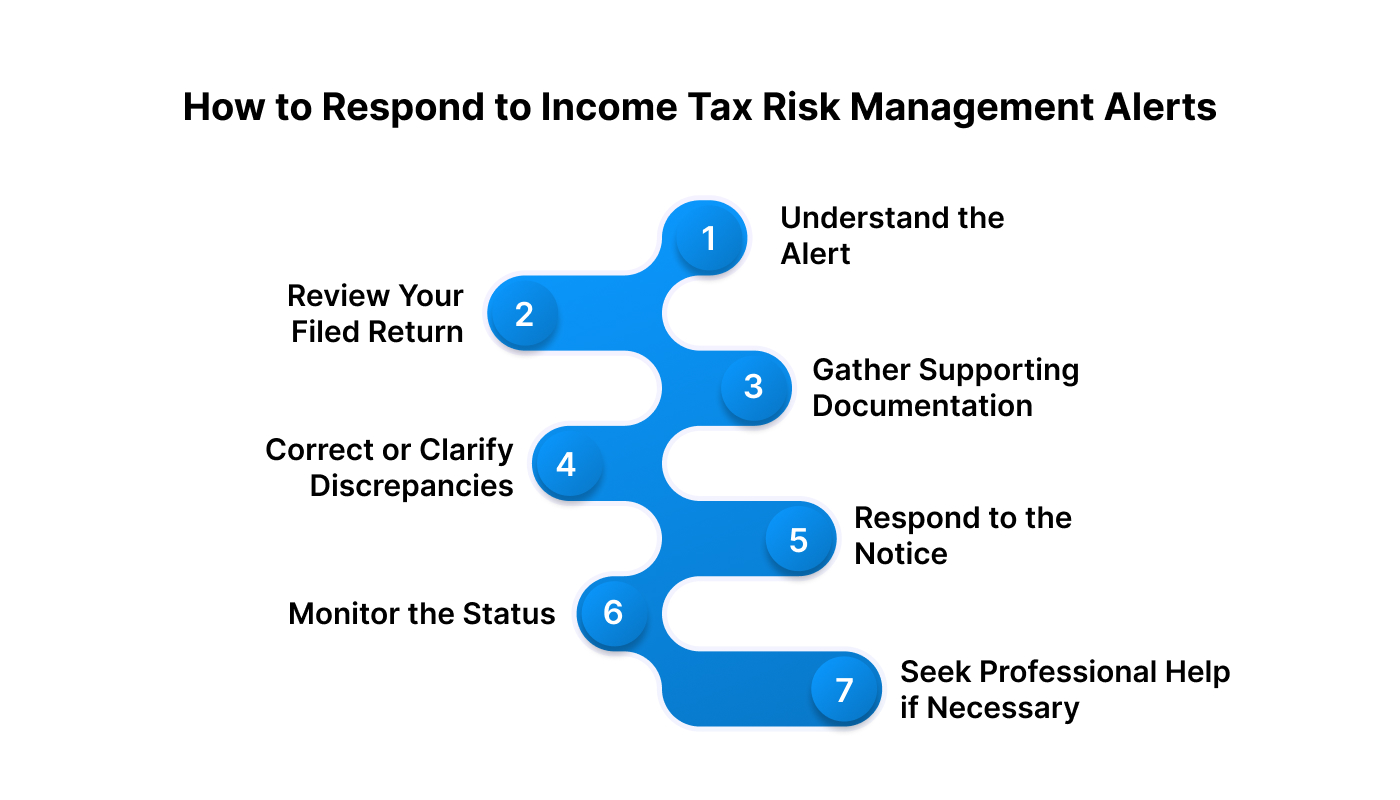
1. Understand the Alert
- Check the Communication: The alert will typically arrive via email, SMS, or e-filing portal notifications. It will explain why your return has been flagged, such as discrepancies in income, deductions, or refund claims.
- Read Carefully: Fully understand the nature of the alert and whether it’s related to missing information, incorrect claims, or other issues. This will determine the next steps.
2. Review Your Filed Return
- Cross-Check Information: Go over your ITR to verify the income reported and compare it with Form 26AS or the Annual Information Statement (AIS) to ensure consistency.
- Identify Any Errors: Look for common issues like overstated deductions, capital gains misreporting, or incorrect tax payments that could be flagged.
3. Gather Supporting Documentation
- Collect All Relevant Proof: If the issue pertains to deductions, exemptions, or income mismatch, ensure that you have all receipts, bank statements, tax certificates, and investment proofs.
- Organise Your Files: Scan or digitise your documents for easy upload and reference when submitting a response.
4. Correct or Clarify Discrepancies
- File a Rectification Request: If the issue is minor, you can correct the error directly by filing a rectified return through the e-filing portal.
- Provide Supporting Documents: If more information is required, upload the necessary documents to validate your claims or explain the discrepancies.
5. Respond to the Notice
- Log in to the E-Filing Portal: After understanding the issue, log in to your Income Tax e-filing account.
- Select the Appropriate Response: Depending on the alert type, you can either submit documents, respond with an explanation, or file a revised return.
- Submit on Time:
- Ensure that you submit your response within the 30-day window to avoid further complications.
6. Monitor the Status
- Track Your Response: After submission, you will receive a confirmation receipt. Keep this for your records.
- Follow Up if Needed: Check for updates on the e-filing portal. If you haven’t received a response within the expected time, consider contacting the Income Tax Helpdesk.
7. Seek Professional Help if Necessary
- Consult a Tax Expert: If the issue is complex or you need expert advice, it may be beneficial to consult with a tax professional to guide you through the process and ensure compliance.
When Tax Time Tightens Your Budget, Pocketly Provides Quick Relief
Tax season can sometimes leave you scrambling to meet deadlines, squeezing your finances and creating temporary cash gaps. When these moments arise, Pocketly offers a fast, easy solution to keep your budget intact without complicating your financial plans.
Pocketly is a digital lending platform offering quick, collateral-free short-term loans ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000. With interest rates starting at just 2% per month and processing fees between 1–8%, you can get the funds you need without the hassle. The approval process is swift, and funds are transferred directly to your bank account within minutes.
Here’s how Pocketly works:
- Quick Sign-Up: Register in just two taps with your mobile number.
- Simple KYC: Upload your Aadhaar and PAN for a quick and easy verification process.
- Bank Details: Add your bank account information securely.
- Flexible Loan Options: Choose your loan amount and repayment tenure.
- Instant Funds Transfer: Get funds directly in your bank account within minutes.
With Pocketly, you get flexible EMIs, no hidden charges, and 24/7 customer support, ensuring that your tax-related cash shortages are handled seamlessly and stress-free.
Bottom Line
Understanding the risk management process in income tax filing not only helps you remain compliant but also keeps your financial journey on track. By familiarising yourself with the verification process, common triggers, and how to respond effectively, you ensure your returns are processed smoothly and avoid unnecessary delays.
The goal is not just to file your taxes correctly but to stay proactive and informed about the system that helps protect both your interests and the country's financial integrity. With this wisdom, you can confidently handle the tax season each year.
If you ever face a cash flow challenge while managing your finances or dealing with tax-related delays, Pocketly is here to help. With quick, small-ticket loans, Pocketly offers a seamless solution to bridge the gap, ensuring your financial plans stay intact.
For easy access to funds during those tight moments, download Pocketly on iOS or Android, always available when you need it most.
FAQs
1. What is the risk management process in income tax?
The risk management process in income tax is an automated system used by the Income Tax Department to screen and flag returns with potential discrepancies or anomalies for further review. It ensures the accuracy of filed returns and prevents fraud.
2. Why was my return flagged in the risk management process?
Your return may be flagged if there are inconsistencies between your reported income and third-party data, unusually high refund claims, or incorrect deductions. This doesn't mean there’s wrongdoing; it simply triggers further verification.
3. What should I do if my return is flagged?
If your return is flagged, you will receive a notification from the Income Tax Department. You should carefully review your return for errors and either confirm the details or file a revised return. You can also respond to the tax department through the e-filing portal.
4. Will my refund be delayed if my return is flagged?
Yes, if your return is flagged, it could delay your refund. However, by responding promptly and addressing the flagged issues, you can accelerate the process and avoid any extended delays.
5. How long do I have to respond to a flagged return?
You should respond to the flagged return within the time frame specified by the Income Tax Department (usually 30 days) to avoid further delays or complications in processing.
6. Is there a penalty for having my return flagged?
Having your return flagged does not automatically result in a penalty. Penalties may only apply if you are found to have intentionally given false or misleading information. As long as you address the flagged items correctly, there should be no penalty.