As digital lending practices grow in India, keeping track of the guidelines set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) becomes crucial for borrowers and lenders alike. The rapid rise of digital lending platforms brings both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, they offer quick access to credit; on the other, they expose users to concerns like data privacy and misrepresentation.
This blog will explore the new RBI Digital Lending Directions, 2025, which aim to tackle these challenges. You'll learn about the guidelines' key provisions, their applicability, and how they contribute to borrower protection and data transparency.
Key Takeaways
- Consumer Protection: The RBI has introduced measures like clear disclosures, grievance redressal mechanisms, and the prohibition of manipulative practices, ensuring a safer borrowing experience for consumers.
- Enhanced Data Privacy: New data protection provisions mandate that digital lending platforms limit data collection to essential information only and store all data within India, ensuring stronger privacy protection.
- Impact of FLDG Cap: The 5% cap on First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG) arrangements poses operational challenges for BNPL platforms and lenders, particularly those catering to high-risk borrowers.
- Digital Lending’s Growth: The digital lending market in India continues to expand, with innovative solutions such as BNPL gaining traction, though the regulatory framework is still evolving to address emerging challenges.
What is Digital Lending?
Digital lending refers to the process of providing loans through online platforms, using digital technologies for a faster, more accessible, and hassle-free experience. It involves the use of technology to offer quick and convenient access to credit, eliminating the need for traditional paper-based processes.
Digital lending platforms rely on data-driven algorithms for credit assessments, making the loan approval process faster and more efficient. These platforms offer personal loans, microloans, or business financing, with minimal documentation and flexible repayment options.
Overview of the RBI's Digital Lending Directions, 2025
The RBI started the Reserve Bank of India (Digital Lending) Directions, 2025, to streamline and regulate digital lending activities in India. These guidelines came into effect on 8th May 2025, with specific provisions related to multi-lender arrangements set to take effect from 1st November 2025, and reporting requirements for Digital Lending Apps (DLAs) starting from 15th June 2025.
The primary objective of these Directions is to strengthen the regulatory structure around digital lending, an automated, technology-driven process that encompasses customer acquisition, credit evaluation, loan approval, disbursement, and recovery.
By formalizing these processes, the RBI aims to ensure greater transparency, security, and consumer protection within the rapidly expanding digital lending ecosystem.
Scope and Applicability of the Digital Lending Guidelines
The RBI's Digital Lending Guidelines of 2025 have brought about a comprehensive framework targeting a broad range of digital lending activities in India. These guidelines are applicable to the following entities:
1. All Commercial Banks
2. All Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks, State Co-operative Banks, Central Cooperative Banks
3. All Non-Banking Financial Companies (including Housing Finance Companies)
4. All All-India Financial Institutions.
Within this regulatory framework, two key players have emerged as central figures in the digital lending ecosystem. The guidelines establish distinct roles for these entities, creating a clear hierarchy of responsibilities and accountability measures.
Roles and Responsibilities of Digital Lending Apps (DLAs) and Lending Service Providers (LSPs)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has delineated specific roles and responsibilities for Digital Lending Apps (DLAs) and Lending Service Providers (LSPs) under the Digital Lending Directions, 2025, aiming to enhance transparency, accountability, and consumer protection in the digital lending ecosystem.
Digital Lending Apps (DLAs)
Digital Lending Apps (DLAs) are mobile or web platforms that act as intermediaries, providing a platform for consumers to access digital lending services. These apps may be operated either directly by Regulated Entities (REs) or through Lending Service Providers (LSPs) working on behalf of the REs.
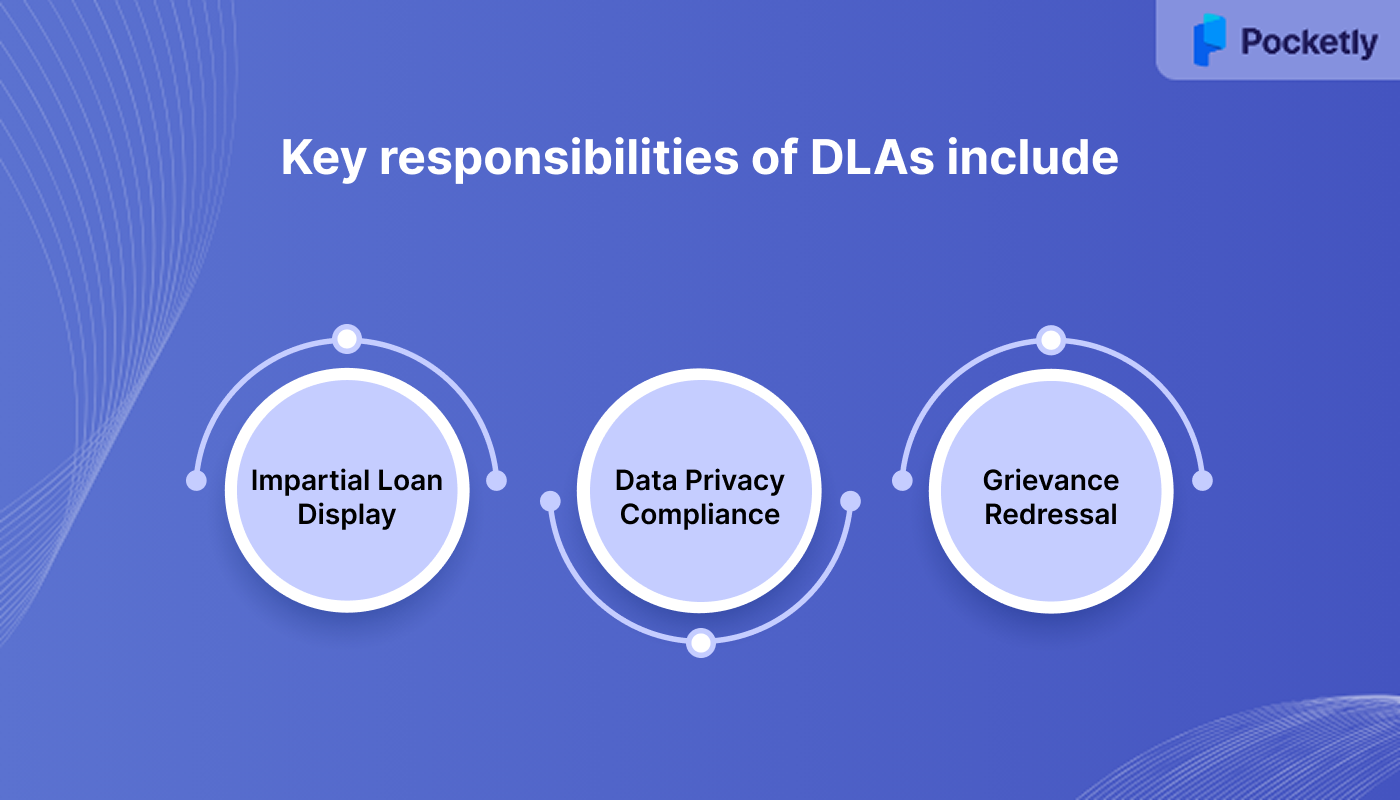
Key responsibilities of DLAs include:
- Impartial Loan Display: Offering clear and transparent information regarding loan terms without bias.
- Data Privacy Compliance: Safeguarding customer data through proper handling and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
- Grievance Redressal: Providing consumers with easy access to grievance redressal and ensuring the timely resolution of complaints.
Lending Service Providers (LSPs)
Lending Service Providers (LSPs) support the functioning of digital lending by offering services such as customer acquisition, loan underwriting, and collections. They must also operate under formal agreements with Regulated Entities (REs), which outline the roles and responsibilities of both parties.
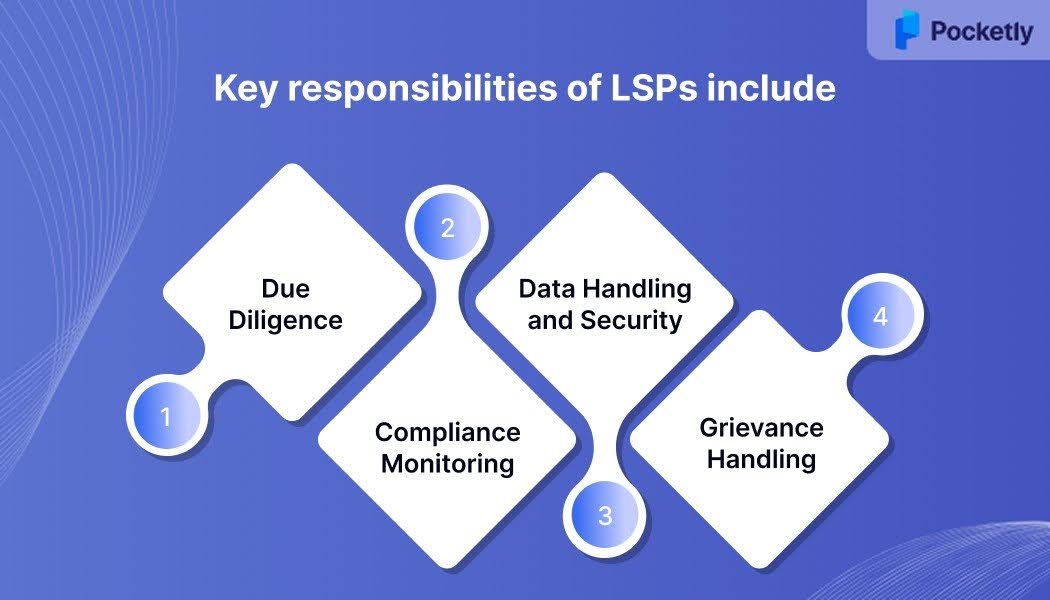
Key responsibilities of LSPs include:
- Due Diligence: Conducting thorough checks to assess the capabilities and compliance of LSPs before entering into contracts.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensuring that LSPs follow regulatory guidelines and the terms outlined in agreements with REs.
- Data Handling and Security: Ensuring that borrower data is collected and processed securely, with explicit consent from the consumer.
- Grievance Handling: Assisting in addressing consumer complaints and providing support in collaboration with the REs.
Both DLAs and LSPs play an integral role in digital lending, with the RBI’s guidelines ensuring that these entities act responsibly, ensuring the protection of consumer rights, and maintaining trust in the system.
Compliance Essentials: Disclosures and Due Diligence
Before executing any loan contract, regulated entities (REs) are required to provide borrowers with a Key Fact Statement (KFS) containing essential loan terms, APR, repayment obligations, charges, and detailed product and privacy policies.
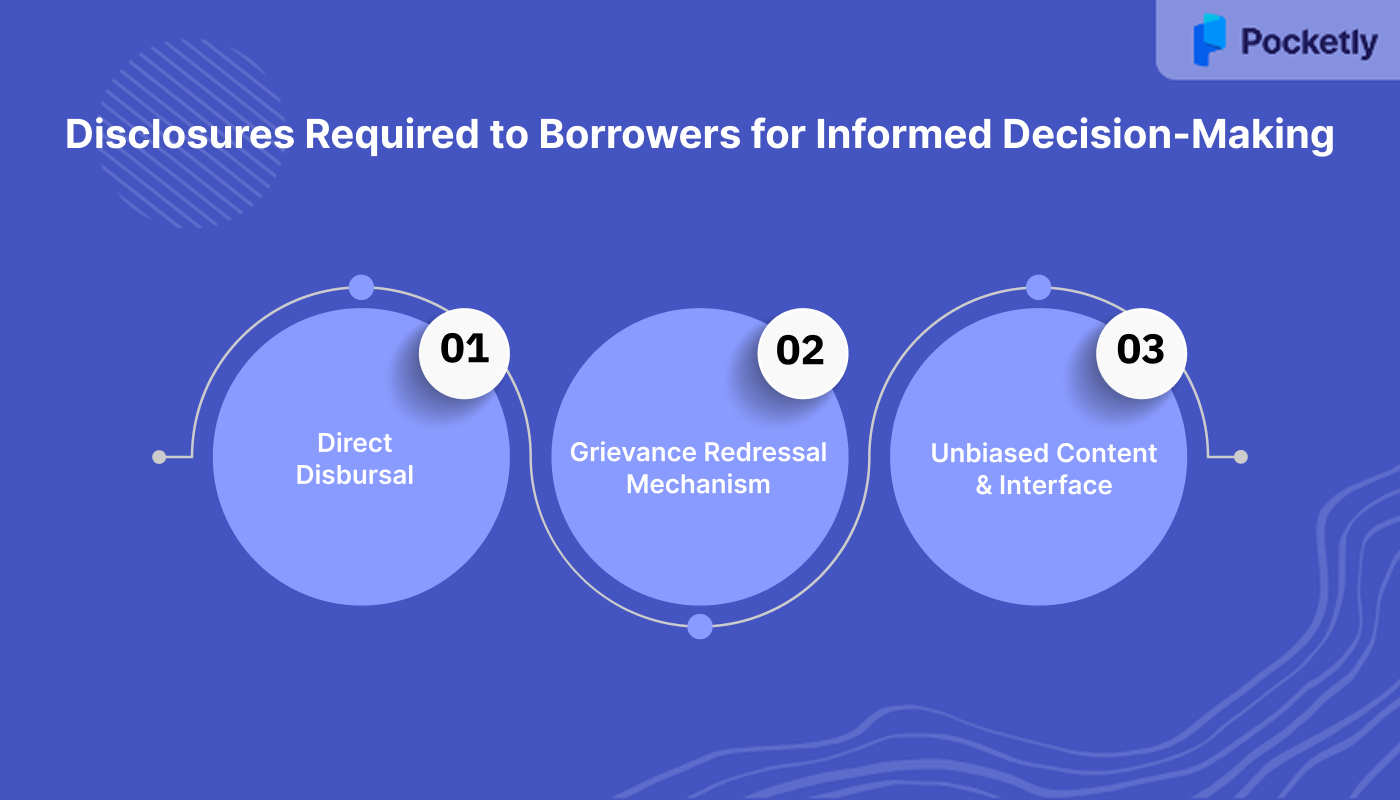
Disclosures Required to Borrowers for Informed Decision-Making
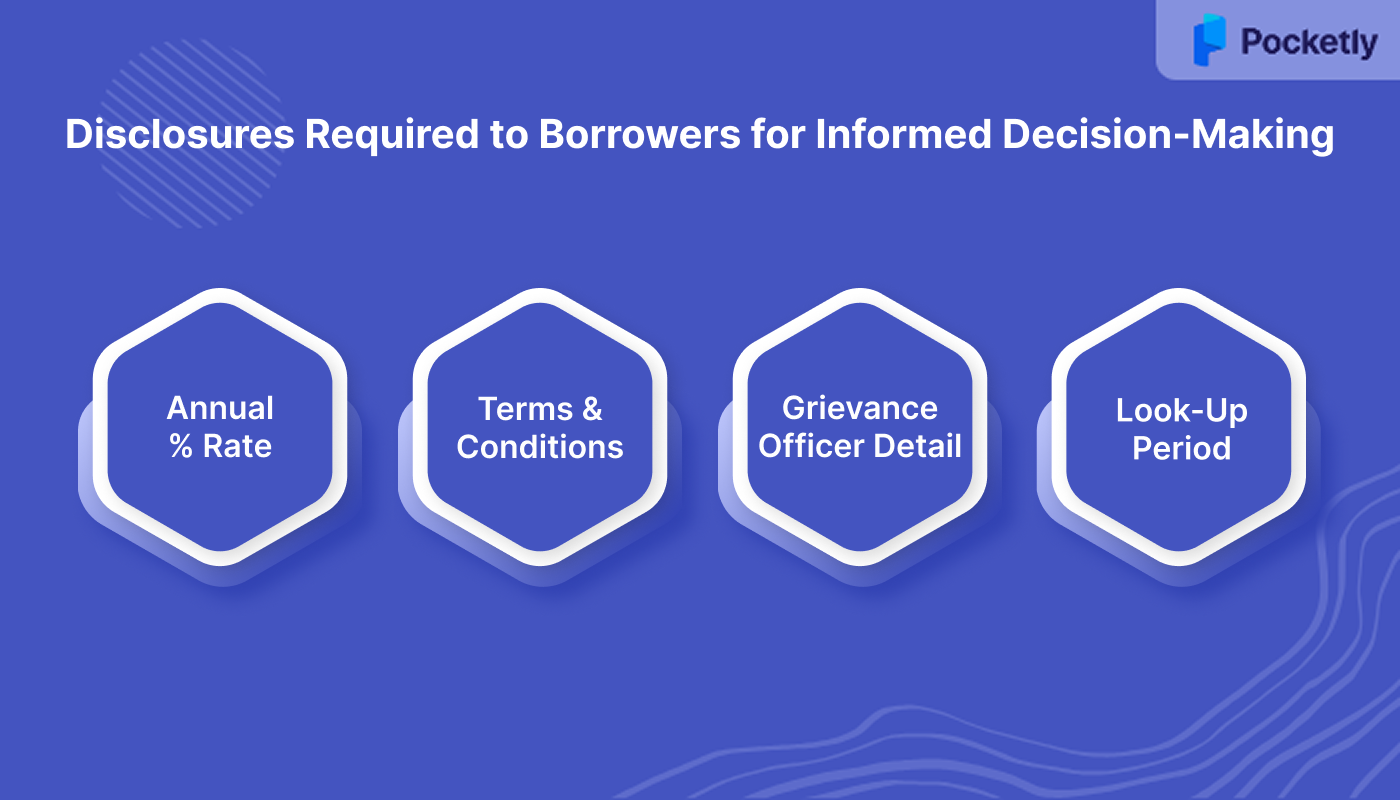
To promote transparency and informed decision-making, the RBI mandates that all digital lending products provide a Key Fact Statement (KFS) to borrowers before the execution of the contract. This KFS must include:
- Annual Percentage Rate (APR): The cost of the loan expressed as an annualized rate, including all associated fees and charges.
- Terms and Conditions of Recovery Mechanism: Clear details about the repayment schedule, penalties for late payments, and the recovery process.
- Grievance Redressal Officer Details: Contact information of the officer designated to handle complaints related to digital lending.
- Cooling-Off/Look-Up Period: A specified period during which the borrower can exit the loan without penalty by paying the principal and proportionate APR.
Additionally, all digitally signed documents supporting important transactions must automatically be sent to the borrower's registered email or phone number.
Enhanced Due Diligence on LSPs' Capabilities and Compliance
Regulated Entities (REs) are required to conduct thorough due diligence before entering into partnerships with LSPs for digital lending. This includes:
- Technical Capabilities: Assessing the LSP's technological infrastructure to ensure secure and efficient operations.
- Data Privacy Policies: Evaluating the LSP's adherence to data protection regulations and to safeguard borrower information.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensuring that the LSP complies with all applicable laws and regulations governing digital lending.
While transparency and due diligence form the operational foundation, the protection of sensitive borrower information represents the most critical aspect of the new regulations. Here are some stringent data protection measures that reshape how personal information is handled throughout the lending lifecycle.
Data Protection, Technology, and Privacy Policy Under the Digital Lending Directions, 2025
The Data Protection, Technology, and Privacy Policy provisions under the RBI’s Digital Lending Directions, 2025, aim to ensure that consumers’ sensitive information is safeguarded throughout the digital lending process.
1. KYC and Data Minimization: One of the major shifts in the new guidelines is the restriction on data collection during the KYC process. Regulated Entities are required to limit the data collected to only what is absolutely necessary. This protects borrower privacy by preventing unnecessary data collection and potential misuse.
2. Consent for Third-Party Sharing: Borrowers must give explicit consent before their data can be shared with any third parties. Personal information, especially sensitive data, should not be stored or shared without clear permission from the borrower.
3. Access Restrictions: DLAs and LSPs are prohibited from accessing borrowers’ sensitive phone data, including media files, contact lists, call logs, and telephony functions. This restriction prevents unnecessary overreach into borrowers' personal information.
4. Comprehensive Privacy Policy: REs are required to ensure that their LSPs have a clear and strong privacy policy. This policy must outline the details of the parties authorized to access borrowers' personal data through the DLAs and ensure that only trusted entities are involved.
5. Data Localization Mandate: To strengthen data protection, the guidelines mandate that all borrower data must be stored within India. If data is processed outside the country, it must be deleted from foreign servers within 24 hours.
6. RE Responsibility for Data Security: Regulated Entities are responsible for ensuring the security and privacy of the borrower’s personal data at all stages of the digital lending process, including the onboarding, loan approval, disbursement, and recovery phases.
The robust data protection framework initiatives extend beyond privacy concerns to address fundamental aspects of fair lending practices and consumer empowerment.
Borrower Protection Initiatives under the RBI Digital Lending Directions, 2025
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has implemented several borrower protection initiatives to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in the digital lending ecosystem. These measures aim to safeguard borrowers' interests and promote responsible lending practices.
- Direct Disbursal and Repayment: All loan disbursements must be made directly into the borrower's bank account, and repayments should be made directly to the Regulated Entity's (RE's) account. This eliminates the involvement of third parties, reducing the risk of misappropriation and enhancing transparency.
- Grievance Redressal Mechanism: REs and their Lending Service Providers (LSPs) are required to appoint grievance redressal officers and display their contact details on their websites, Digital Lending Apps (DLAs), and Key Fact Statements (KFS). Borrowers can escalate unresolved complaints to the RBI's Complaint Management System (CMS) or send a physical complaint to the RBI's office.
- Unbiased Content and Interface: DLAs and LSPs must present loan offers impartially, displaying all available options without promoting specific lenders. They are prohibited from using deceptive practices or "dark patterns" that mislead borrowers into choosing particular loan offers.
Despite the comprehensive nature of these guidelines, their implementation has created operational challenges for various stakeholders in the digital lending ecosystem. Industry players are grappling with compliance requirements while seeking clarity on specific aspects of the regulations.
Industry Challenges and Clarifications under RBI’s Digital Lending Directions, 2025
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Digital Lending Directions, 2025, have introduced a structured regulatory framework for digital lending. However, these regulations have also presented certain challenges and raised the need for clarifications, concerning payment aggregators, Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) platforms, and the First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG) arrangements.
Challenges Faced by Payment Aggregators and BNPL Platforms
- Direct Fund Flow Mandate: The RBI mandates that loan disbursals and repayments must occur directly between the borrower and the Regulated Entity (RE), excluding third-party intermediaries. This restriction impacts payment aggregators and BNPL platforms that previously facilitated transactions through wallets or non-bank fintech accounts.
- Operational Model Overhaul: Fintechs operating BNPL services, such as Slice and Uni, which utilized open-loop, card-based BNPL models, have been compelled to revise their business structures. The prohibition of loading Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) with credit lines has necessitated significant changes in their operational models.
Clarifications Needed on FLDG Arrangements and Operational Models
- FLDG Cap and Applicability: The RBI has set a cap of 5% on the total amount of FLDG cover for any outstanding loan portfolio. This cap applies to the total amount disbursed out of the FLDG set at any given time. The guidelines specify that the portfolio over which FLDG can be offered must consist of identifiable and measurable loan assets, remaining fixed for the purpose of the specific FLDG arrangement.
- Reinstatement of FLDG: Once the FLDG amount is invoked due to a default, the subsequent recoveries made from borrowers on the defaulted amount cannot be added back to the FLDG cover. This stipulation limits the ability to replenish the FLDG after it has been utilized.
- Regulatory Compliance for LSPs: The guidelines require that Lending Service Providers (LSPs) engaged by REs comply with the Digital Lending Directions. This includes that LSPs do not have control over the flow of funds between the borrower and the RE and that they adhere to the prescribed conduct and customer protection requirements.
These challenges and the need for clarifications aim to protect borrowers and ensure responsible lending; they also necessitate adjustments and clarifications to accommodate the operational models of fintech companies and to instill a balanced and sustainable digital lending ecosystem.
Why Choose Pocketly for Your Digital Lending Needs?
Pocketly offers a reliable and flexible solution for managing your short-term financial needs with quick access to loans and transparent terms. With a focus on convenience, affordability, and transparency, Pocketly empowers young Indians to take control of their financial journey, whether you need a small loan for personal expenses or a larger amount to manage business cash flow.
- Loan Amounts: Pocketly provides loans ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000, catering to a variety of financial needs.
- Competitive Interest Rates: Enjoy interest rates starting from just 2% per month, ensuring affordable repayment options.
- Flexible Processing Fees: Processing fees range from 1% to 8% of the loan amount, based on the loan size and repayment terms, with no hidden charges.
- No Collateral: All loans are unsecured, so you don’t need to provide collateral, making the process simpler and quicker.
- Quick Approval: Get instant personal loan approval and quick disbursement with minimal documentation and an easy KYC process.
- Flexible Repayment Options: Choose from various repayment plans that suit your financial situation, with the ability to pay early or partially without penalties.
- 24/7 Support: Access round-the-clock customer support to assist with any queries or issues during the loan process.
Conclusion
Digital lending is rapidly evolving in India, offering consumers greater access to credit, convenience, and flexibility. The RBI’s Digital Lending Directions, 2025, have been introduced to regulate this space and ensure consumer protection, transparency, and secure data practices.
These guidelines address crucial aspects such as loan disbursement, borrower consent, grievance redressal, and the role of Digital Lending Apps (DLAs) and Lending Service Providers (LSPs). As the ecosystem grows, these measures aim to create a fair, accountable, and consumer-friendly lending environment, balancing innovation with safeguards.
Pocketly, as a digital lending platform that offers flexible loan amounts, transparent terms, and quick disbursements, is here to support your financial needs. Download the Pocketly app now on iOS or Android to access quick and easy loans today!
FAQs
1. What are the rules for digital transactions in RBI?
RBI guidelines for digital transactions ensure secure, transparent, and efficient payment systems. They mandate the use of encryption, strong customer authentication (SCA), and compliance with data protection laws to protect consumers from fraud and data breaches.
2. What is the process of digital lending?
Digital lending involves applying for a loan via an online platform, with quick approval using automated credit scoring and real-time data processing. Loans are disbursed directly to the borrower’s bank account, with flexible repayment options offered.
3. What is the role of AI in digital lending?
AI in digital lending helps automate credit assessments, analyze borrower data for risk profiling, and provide personalized loan offers. It improves efficiency, reduces human error, and enhances decision-making for faster, more accurate loan approvals.
4. What are the directions of RBI on digital lending 2025?
The RBI’s Digital Lending Directions, 2025, aim to regulate digital lending activities, ensuring transparency, fair practices, and consumer protection. These directions cover aspects such as loan disbursements, grievance redressal, data protection, and the roles of Digital Lending Apps and Service Providers.
5. What is the RBI lending Directive?
The RBI lending directive mandates that, starting in 2026, borrowers will no longer be charged prepayment fees on floating-rate loans for personal use. The directive prohibits banks and regulated lenders from imposing such charges, offering more flexibility to borrowers.