Securing a personal loan is one of the most important financial decisions you’ll make, but with multiple lending options available, it’s important to choose the right fit for your needs.
In India, both Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and traditional banks offer personal loans, but each comes with its own set of advantages. As of March 2024, NBFCs accounted for 71.2% of the total loan portfolio in sectors like retail and industry, highlighting their substantial role in the lending system.
Without a clear understanding of the differences between the two, you may face higher interest rates, stricter eligibility criteria, or slower loan processing times, all of which can impact your financial goals.
Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, or individual seeking financial support, recognising these differences can help you select the right financial partner for your future.
Key Takeaways
- NBFCs vs Banks: NBFCs offer faster loan approvals and more flexible eligibility criteria, making them ideal for borrowers with limited credit history or urgent financial needs. Banks provide a wider range of services but have stricter loan approval processes.
- Loan Processing Speed: NBFCs are known for quicker loan processing with minimal documentation, while banks follow a more rigorous approval process.
- Interest Rates and Fees: Banks typically offer lower interest rates due to regulated funding sources, while NBFCs charge higher rates to offset their higher risk but provide more flexibility in loan terms.
- Security and Insurance: Bank deposits are insured up to ₹5 lakh by DICGC, offering greater security, while NBFC deposits are not insured.
- Which to Choose: If you need quick loans and specialised products, NBFCs are a good fit. For long-term financing with lower interest rates and insured deposits, banks are the better option.
Overview of Banks and NBFCs
Banks are financial institutions licensed and regulated by government authorities, such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), that can accept deposits from the public, extend loans, and offer a wide range of financial services like savings accounts, fixed deposits, etc.
Examples of banks in India:
- State Bank of India (SBI)
- HDFC Bank
- ICICI Bank
- Axis Bank
On the other hand, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) are financial institutions that provide financial services, such as personal loans, asset management, and investment products. Unlike banks, they do not hold a banking license and cannot accept deposits from the public.
Examples of NBFCs in India:
- Bajaj Finance
- Muthoot Finance
- HDFC Ltd. (Housing Finance)
- Shriram Transport Finance
While both institutions serve the financial sector, their operational frameworks and service offerings differ significantly.
Key Difference Between NBFC and Bank: Which Financial Institution Is Right for You?
Choosing between a bank and an NBFC can be a critical decision based on your financial needs. If you seek a broad set of services and can meet the stringent criteria, banks may be your best bet. But if you need faster access to loans with more relaxed terms, NBFCs might be the right choice.
Here is a comprehensive comparison highlighting the difference between the two.
| Distinguishing Factors | Bank | NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Company) |
| Deposit Acceptance | Authorised to accept demand deposits (e.g., savings and current accounts). | Cannot accept demand deposits; focuses on lending and investment activities. |
| Payment System Access | Part of the payment and settlement system; it can issue cheques drawn on itself. | Not part of the payment and settlement system; cannot issue cheques drawn on itself. |
| Reserve Requirements | Must maintain Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) as mandated by the RBI. | Not required to maintain CRR or SLR. |
| Foreign Investment | FDI is permitted up to 74% of the paid-up capital. Within this, up to 49% is allowed under the Automatic Route | FDI allowed up to 100%, subject to sectoral caps and conditions. |
| Priority Sector Lending | Obligated to lend a portion of their credit to the priority sector (e.g., agriculture, micro, small, and medium enterprises). | Not mandated to lend to the priority sector. |
| Financial Services | Offers a wide range of services, including savings and current accounts, fixed deposits, loans, insurance, and investment products. | Primarily focuses on lending, asset financing, and investment services. |
| Loan Processing | Follows a rigorous loan processing procedure with stringent eligibility criteria. | Offers easier loan approval with relaxed eligibility criteria and faster processing times. |
| Interest Rates | Offers lower interest rates due to regulated funding sources and lower risk. | Higher interest rates to compensate for higher risk and unregulated funding sources. |
| Lending Focus | Offers a wide range of loans (personal, home, business, education) | Focuses on niche lending (personal loans, small business loans, asset-backed financing) |
These structural differences translate into tangible benefits for consumers depending on their financial priorities. Banks, with their comprehensive regulatory framework and diverse service portfolio, offer distinct value propositions.
Also Read: Quick NBFC Personal Loans for People with Bad Credit Score in India
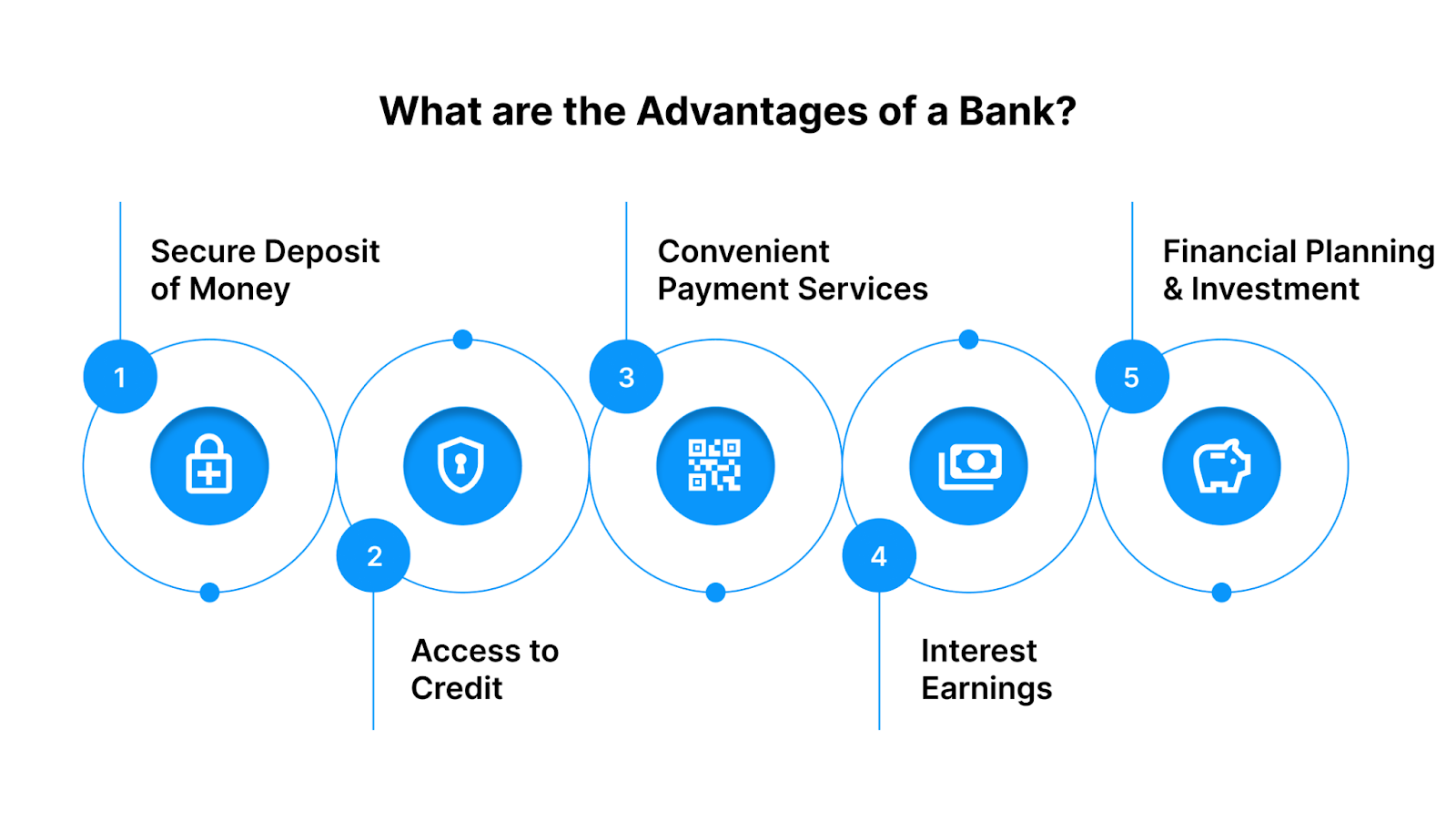
Banks offer several key advantages, making them a reliable choice for individuals and businesses alike. They provide a wide range of financial products such as savings and checking accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment services under a secure and regulated environment.
- Secure Deposit of Money: Banks provide a safe place to deposit your savings, protecting your funds from theft or loss.
- Access to Credit: Banks offer various loan products, including personal, business, home, and education loans, helping individuals and businesses meet financial needs.
- Convenient Payment Services: Banks facilitate payments through cheques, NEFT, RTGS, UPI, and debit/credit cards, making transactions faster and easier.
- Interest Earnings: Deposits in savings and fixed deposit accounts earn interest, allowing customers to grow their funds over time.
- Financial Planning and Investment Services: Banks provide advisory services, mutual funds, insurance, and investment options to help customers plan their financial future.
While banks excel in providing secure financial solutions, NBFCs have carved out their own niche by addressing gaps in accessibility and speed. Their operational flexibility makes them appealing in certain scenarios.
Advantages of Choosing an NBFC over a Bank
Choosing between an NBFC and a bank largely depends on your financial needs and situation. If you require quick loan approval with minimal documentation or if you have a limited credit history, NBFCs are often more flexible and quicker to process.
- Quick Loan Approval: If you need a loan urgently, NBFCs tend to have faster approval times and fewer documentation requirements compared to banks.
- Flexible Eligibility Criteria: If you have a limited credit history, irregular income, or if you are a new borrower, NBFCs may be more willing to approve your loan, even if you don't meet all of the strict criteria required by banks.
- Specialised Loan Products: For specific loans such as gold loans, vehicle loans, or small-ticket personal loans, NBFCs often provide tailored financial products that banks may not offer or might take longer to approve.
- Higher Loan Amounts for Asset-Backed Financing: If you need financing based on assets like property or gold, NBFCs tend to offer higher amounts with minimal paperwork, making them ideal for individuals seeking asset-based loans.
- Easier Documentation: If you’re looking for a loan with minimal documentation and simpler procedures, NBFCs can provide quicker access to funds with fewer hurdles than banks.
Beyond individual lending, NBFCs contribute significantly to India's broader economic system through diverse financial services.
Functions of NBFCs in India
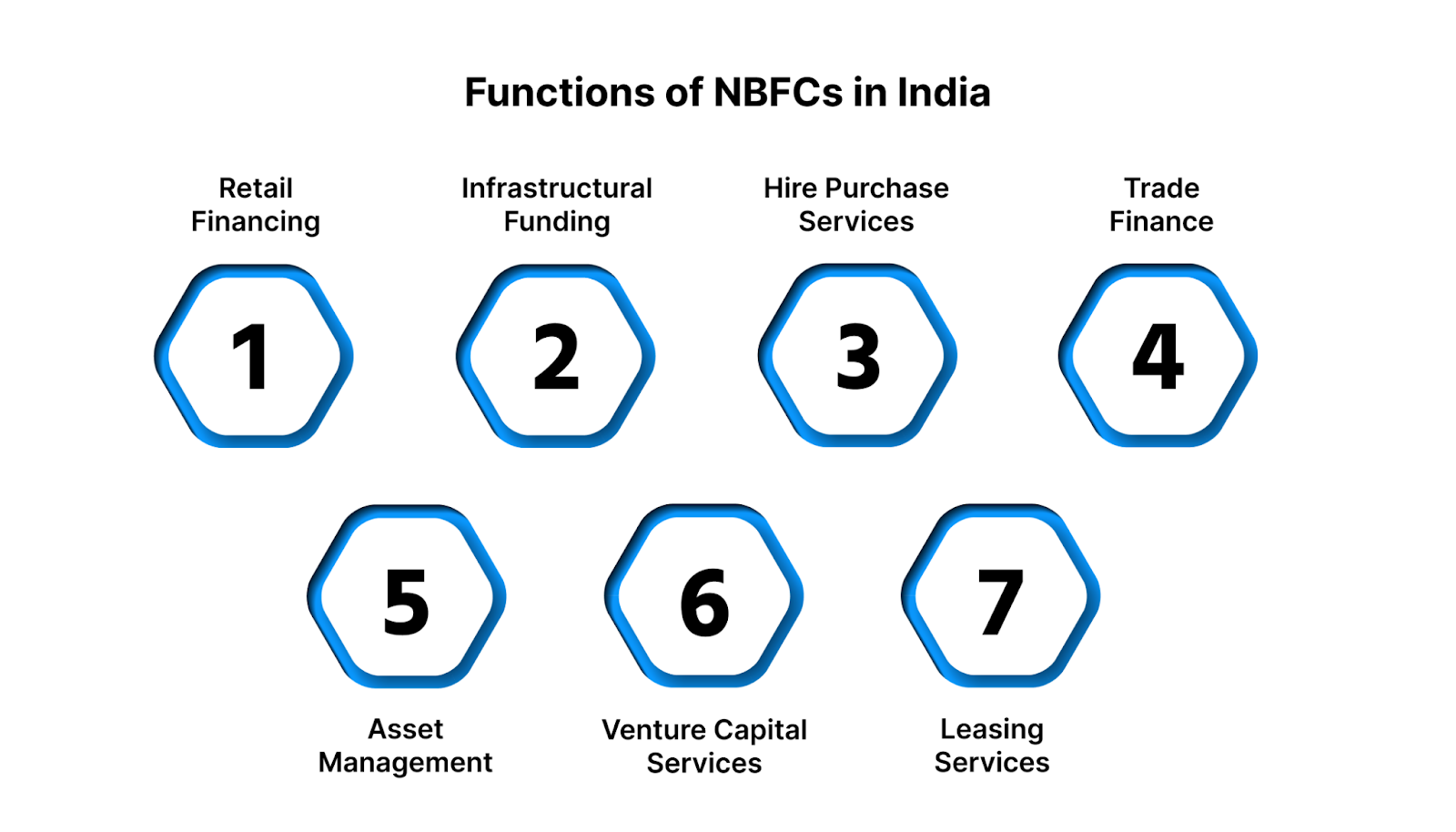
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) play a pivotal role in India's financial ecosystem by offering a range of services that complement traditional banking institutions. They are instrumental in improving financial inclusion and catering to the underserved segments of society.Retail Financing: NBFCs provide short-term loans to individuals and businesses for various purposes, such as loans against gold, shares, and property, primarily to meet consumption needs.
- Retail Financing: NBFCs provide short-term loans to individuals and businesses for various purposes, such as loans against gold, shares, and property, primarily to meet consumption needs.
- Infrastructural Funding: They allocate substantial funds to infrastructure projects, including railways, metros, real estate developments, ports, flyovers, and airports, contributing to the nation's infrastructure growth.
- Hire Purchase Services: NBFCs facilitate hire purchase services, allowing buyers to acquire goods by making payments in installments, with ownership transferring upon completion of payments.
- Trade Finance: They offer trade finance solutions, particularly distributor or dealer finance, to support businesses in managing their vendor finance, working capital requirements, and other business loans.
- Asset Management: NBFCs operate as Asset Management Companies, managing funds pooled from small investors and investing primarily in equity shares to generate returns.
- Venture Capital Services: Certain NBFCs engage in venture capital services by investing in small businesses at their initial stages, inspiring entrepreneurship and innovation.
- Leasing Services: They offer leasing services, providing properties and assets to businesses that may not have the resources to purchase them outright, enhancing operational capabilities.
The diverse functions performed by NBFCs operate within a distinct regulatory environment that differs from traditional banking. These regulatory variations shape how each institution manages risk, capital, and consumer protection.
Regulatory Differences Between NBFCs and Banks: What You Need to Know
Understanding the regulatory framework governing Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and banks is crucial for individuals and businesses when selecting the right financial institution.
While both are key players in the financial sector, they operate under distinct regulations designed for stability, consumer protection, and sound financial practices.
| Comparison Aspects | NBFC | Bank |
| Regulatory Body | Reserve Bank of India (RBI) oversees NBFCs under the RBI Act, 1934. | RBI regulates Commercial Banks. Cooperative Banks are overseen by both RBI and NABARD. RRBs are regulated by RBI, NABARD, and State Governments. |
| Capital Adequacy | Minimum capital adequacy ratio as prescribed by the RBI varies by type and size of NBFC. | Banks must maintain a higher capital adequacy ratio, typically under Basel III norms, to cover risk exposure. |
| Deposit Insurance | NBFC deposits are not insured, no coverage by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC). | Bank deposits are insured up to ₹5 lakh per depositor by DICGC, providing security for depositors. |
| Prudential Norms | Adhere to flexible prudential norms set by the RBI, with less strict regulations compared to banks. | Banks follow stricter prudential norms, including asset classification, provisioning, and reporting standards. |
With these regulatory and operational differences in mind, the decision between banking with a traditional institution or an NBFC becomes clearer. Your financial circumstances and goals will guide this choice.
Also Read: Self-Regulation in RBI's FinTech Framework Explained
Bank vs NBFC: Which One is Right for You?
The choice between a bank and an NBFC ultimately depends on your specific financial needs. If you need quick access to a loan with minimal documentation and have a limited credit history, an NBFC would be a better fit.
On the other hand, if you're looking for lower interest rates, security (with deposit insurance), and a full range of banking services, a bank would likely be the right choice. For example, if you’re a business owner seeking a working capital loan, an NBFC may offer faster processing.
However, for more long-term financing such as a home loan, a bank would be preferable due to its lower rates and stable lending structure.
For those seeking the agility and accessibility of an NBFC with modern digital convenience, innovative platforms are reshaping how Indians access credit.
Pocketly: Your Digital Lending Partner for Quick and Flexible Personal Loans
Pocketly is a digital-first lending platform to meet the financial needs of young professionals, students, and entrepreneurs in India. With a focus on simplicity and speed, Pocketly offers a fully online loan application process, ensuring that users can access funds swiftly and securely.
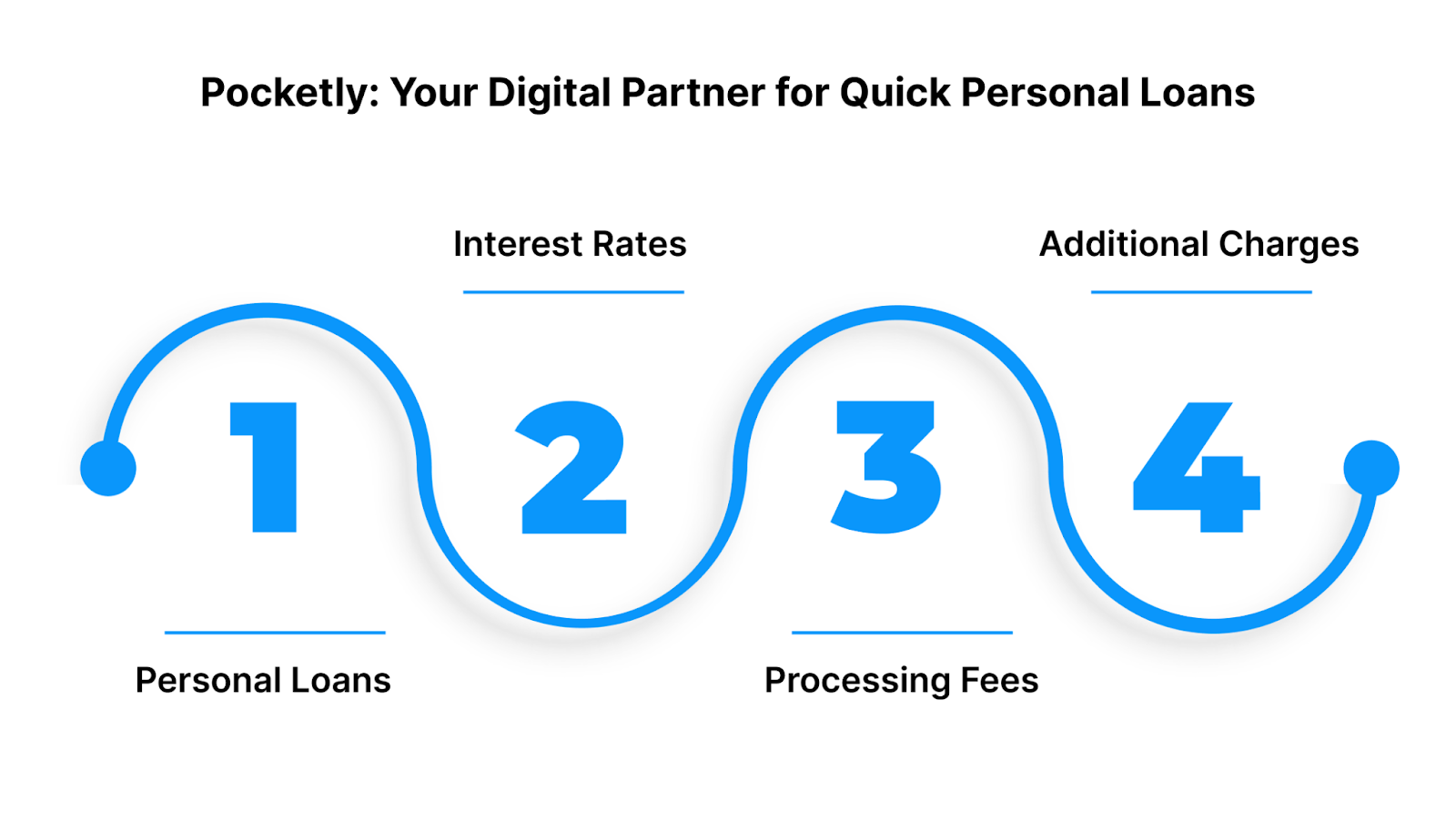
- Personal Loans: Access loans ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000 with flexible repayment options and minimal documentation.
- Interest Rates: Pocketly offers competitive interest rates starting at 2% per month, tailored to your credit profile, loan amount, and tenure. This transparent rate structure allows you to plan your repayments confidently.
- Processing Fees: A minimal processing fee ranging from 1% to 8% of the loan amount is deducted upon approval to cover administrative costs.
Example: For a ₹10,000 loan with a 3% monthly interest rate over 60 days, the total repayment amount would be approximately ₹10,600, including interest and processing fee.
- Additional Charges: Late EMI payments may incur overdue charges, and bounced NACH payments are subject to a nominal fee.
Conclusion
In this blog, we've explored the key differences between NBFCs and banks, focusing on aspects such as regulatory frameworks, loan processing, interest rates, and their respective strengths in the financial ecosystem.
Banks offer a wide range of services with a high level of security and NBFCs provide quicker loan approval, more flexible eligibility criteria. Ultimately, choosing the right financial institution comes down to your specific needs, whether it’s the comprehensive offerings of a bank or the speed and flexibility of an NBFC.
If you’re looking for a quick and flexible personal loan, Pocketly offers an instant personal loan solution with easy application processes and approvals. Download Pocketly now on iOS or Android to get started on your financial journey today!
FAQs
1. Why is NBFC not a bank?
NBFCs are financial institutions regulated by the RBI but do not hold a banking license, which means they cannot accept demand deposits or offer payment services like banks.
2. Can NBFC issue cheques?
No, NBFCs cannot issue cheques as they are not part of the payment and settlement system, unlike banks that are authorised to do so.
3. Can NBFC give home loans?
Yes, certain NBFCs, especially those in the housing finance sector, offer home loans, but their terms and conditions may differ from those of traditional banks.
4. Do NBFCs report to CIBIL?
Yes, NBFCs report borrower credit information to CIBIL and other credit bureaus, helping build a credit history and affect the borrower’s credit score.
5. What is the maximum loan amount for NBFC?
The maximum loan amount that an NBFC can offer depends on the type of loan and borrower eligibility, but typically ranges from ₹1,000 to ₹50,00,000, with higher amounts available for asset-backed loans.