Managing financial risks and optimizing returns is a constant challenge for both businesses and investors. Nowadays, swaps have become one of the most powerful tools to address these challenges. But what exactly are swaps, and how can they benefit both individuals and companies?
A swap is a financial agreement where two parties exchange cash flows or financial instruments over a specified period, typically to manage exposure to various risks. From hedging against interest rate fluctuations to securing favorable exchange rates, swaps provide a range of strategies to protect assets and maintain financial stability.
In this blog, we'll break down the different types of swaps, how they work, and why they are integral to modern financial strategies. If you're looking to understand how swaps can be utilized to your advantage, you've come to the right place.
TL;DR (Key Takeaways)
- A swap is a financial contract where two parties exchange cash flows based on different financial instruments to manage risk, such as interest rates, currency, or commodity prices.
- The most common types of swaps are interest rate swaps, currency swaps, commodity swaps, and equity swaps. Each type serves a unique purpose in financial strategies, such as hedging or speculating.
- Swaps allow for flexibility, low transaction costs, and efficient risk management. They also provide an avenue for firms to access new markets and manage financial exposure.
- While swaps offer significant benefits, they come with counterparty risk, limited liquidity, and potential credit risk. Institutions must weigh these risks carefully to avoid substantial losses.
- For businesses or individuals seeking simpler financial solutions without the complexity of swaps, platforms like Pocketly offer fast, flexible loans with minimal documentation.
What is a Swap?
As we have already said, a swap is a financial contract in which two parties agree to exchange future cash flows or liabilities based on specific, agreed-upon terms. The main objective behind swaps is to help manage financial risk or optimize returns through various financial instruments.
Swaps are designed to allow one party to exchange a stream of payments with another party, typically to benefit from the differences in the rates or terms of various financial instruments. This can involve exchanging interest rate payments, currencies, commodities, or other assets.
The flexibility and customization available in swaps make them powerful tools for businesses, investors, and financial institutions. However, swaps can be complex, and their effectiveness depends on various market factors, including the structure of the swap and the financial health of the counterparties involved.
Now that we have a clear understanding of what swaps are and their role in financial risk management, let’s explore the various types of swaps available in the financial market.
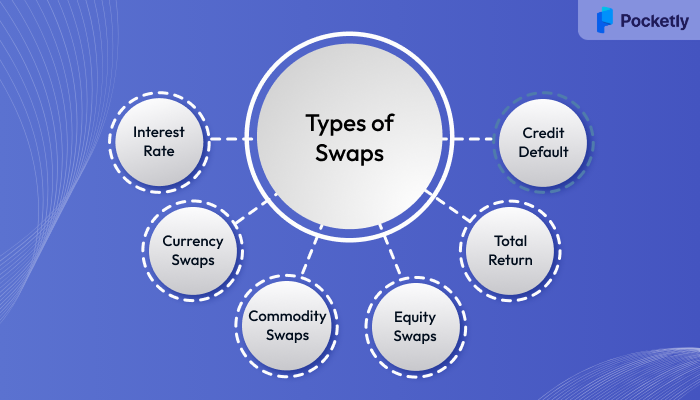
Types of Swaps
Swaps are financial contracts that allow two parties to exchange cash flows or financial instruments over a specified period. The various types of swaps are designed to address different market needs, whether it's for hedging risk, managing interest rate exposure, or seeking favorable currency movements. Below are the most common types of swaps:
1. Interest Rate Swaps
This is the most widely used swap, where two parties exchange fixed interest rate payments for floating rate payments or vice versa. The goal is often to hedge against interest rate fluctuations.
- When to Use: Typically used by companies or institutions that want to alter the interest rate profile of their debt. For example, a company with a floating-rate loan may enter into an interest rate swap to switch to a fixed rate to avoid rising interest rates.
- Benefit: Helps manage interest rate risks by allowing borrowers to swap their interest rate structure to something more predictable.
2. Currency Swaps
Currency swaps involve exchanging cash flows in different currencies, typically in the form of interest payments and principal repayments. One party may pay in one currency, and the other pays in a different currency.
- When to Use: Commonly used by businesses operating in multiple countries to hedge currency risk or to obtain favorable interest rates in foreign currencies.
- Benefit: Facilitates access to better financing rates in foreign currencies and protects against currency fluctuations.
3. Commodity Swaps
Commodity swaps allow parties to exchange cash flows based on the price of a commodity such as oil, gold, or natural gas. Typically, one party will pay a fixed price, while the other pays a price that fluctuates with the commodity's market price.
- When to Use: Widely used by companies exposed to commodity price volatility, such as oil producers or airlines.
- Benefit: Provides companies with protection against commodity price fluctuations, ensuring budget stability for raw materials.
4. Equity Swaps
Equity swaps involve the exchange of cash flows based on the performance of an equity index or specific stock. One party may pay the return of a stock or equity index, while the other pays a fixed interest rate.
- When to Use: Typically used by institutional investors looking to gain exposure to equities without directly owning them. They are often used for hedging or to gain access to equity returns in a tax-efficient manner.
- Benefit: Provides the potential for equity-like returns without needing to actually invest in the underlying equities.
5. Total Return Swaps
In a total return swap, one party agrees to pay the total return (capital gains and income) on an asset, such as a stock or bond, in exchange for a regular cash flow, often a fixed or floating interest payment.
- When to Use: Often used by hedge funds or investors who want to gain exposure to an asset without owning it directly, or to hedge specific risks.
- Benefit: Allows the transfer of both the risk and reward of an asset without actual ownership, offering greater flexibility for investors.
6. Credit Default Swaps (CDS)
A credit default swap is essentially an insurance policy against the default of a debtor. The buyer of a CDS makes periodic payments to the seller in exchange for protection against the default of a borrower (such as a corporation or government entity).
- When to Use: Used by investors looking to hedge credit risk or speculate on the creditworthiness of a company or government.
- Benefit: Provides protection for the buyer of the swap against the risk of default.
These are just a few of the primary types of swaps, each serving a unique purpose depending on the specific financial needs and risk management goals of the parties involved. Let’s now explore how swaps offer distinct advantages for these entities, from managing risk to optimizing capital usage.
Also Read: Flat Vs Reducing Interest Rate Difference
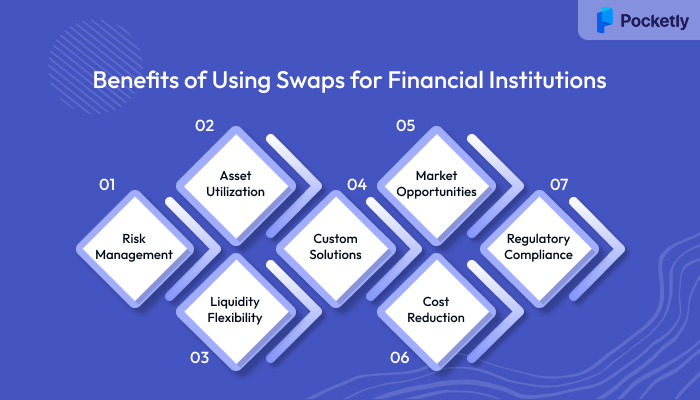
Benefits of Using Swaps for Financial Institutions
Swaps might sound complex, but they’re essentially tools that financial institutions use to make their financial strategies simpler and safer. Here's how swaps benefit banks, lenders, and other financial players in a more accessible way:
1. Managing Risks
One of the key reasons financial institutions use swaps is to manage risks like changes in interest rates or currency values. If a bank is worried that interest rates might go up, they can use swaps to "lock in" a fixed rate, making their financial planning more predictable. This helps them avoid sudden financial shocks.
2. Better Use of Available Funds
Instead of spending a large amount of money upfront to buy assets (such as properties or stocks), swaps enable institutions to access the same benefits without actually purchasing them. This way, they can save money and use it for other important purposes, such as lending or expanding their services.
3. Staying Liquid and Flexible
Banks and financial institutions must ensure they have sufficient cash to meet their daily needs and lend money to others. Swaps help them balance their finances by protecting them from sudden changes in the market (like interest rate hikes) while ensuring they can still meet their obligations.
4. Custom Solutions for Financial Needs
Every financial institution has different needs, and swaps are flexible enough to meet those. For example, if a bank needs to protect itself from currency fluctuations or rising interest rates, swaps can be customized to suit those needs, ensuring they’re always ready for what the market throws their way.
5. Benefiting from Market Changes
Swaps can also be used to take advantage of favorable market conditions. For example, if a bank sees an opportunity where interest rates are dropping, swaps can help them lock in favorable rates, potentially boosting their profits.
6. Lowering Borrowing Costs
Swaps can also help financial institutions reduce their borrowing costs. By using swaps to switch from variable interest rates to fixed rates, they can avoid paying more if interest rates go up in the future.
7. Compliance with Financial Rules
Regulatory rules are becoming increasingly stringent for financial institutions, and swaps enable them to remain compliant. By using swaps to manage their financial risks, they can meet the necessary regulatory standards and avoid penalties, keeping their operations smooth and trouble-free.
While swaps provide numerous benefits to financial institutions, they are not without their challenges. To fully use swaps, institutions must be aware of the risks and hurdles that can affect their immediate financial standing and long-term strategy.
If you’re looking for an immediate solution to financial challenges, Pocketly can provide you with quick and hassle-free loans. With flexible terms and minimal documentation, Pocketly helps you manage liquidity without the complexities of traditional financial instruments. Get started today!
Challenges and Risks of Using Swaps
Swaps are valuable tools for managing finances, but they do come with certain risks. These risks must be carefully understood and managed to avoid financial losses. Let's break down some of the key risks associated with swaps:
- Counterparty Risk
The Problem: Sometimes, the other party in a swap agreement might not fulfill their end of the deal. This can result in significant financial losses, especially if the swap involves a substantial amount of money or is established over an extended period.
The Solution: Before entering into a swap, it's important to assess the financial stability and reliability of the other party. Institutions need to ensure that the counterparty can meet their obligations.
- Market Risk
- The Problem: Swaps are sensitive to changes in the market, such as shifts in interest rates or currency values. If the market doesn’t move as expected, institutions could face losses.
- The Solution: Financial institutions can manage this risk by closely monitoring market trends and doing thorough research. This will help them make informed decisions and better predict market movements.
- Liquidity Risk
- The Problem: In some cases, swaps can make it hard to access cash when needed, especially if the market moves unfavorably. If an institution wants to reverse a swap and there is no one willing to take the other side, it could face liquidity issues.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, institutions should ensure they have enough liquidity on hand and should work with multiple counterparties to increase the chances of reversing swaps if necessary.
- Complexity and Management Costs
- The Problem: Some swaps are highly complex, particularly those that are customized. Managing these swaps can require specialized knowledge and expertise, which can be costly and time-consuming.
The Solution: Financial institutions can reduce complexity by working with experienced teams or outsourcing swap management to experts. This way, they can avoid unnecessary costs and ensure the swaps are being managed correctly.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks
- The Problem: As financial regulations continue to evolve, swaps must comply with strict rules to avoid penalties. Failing to comply with regulations can result in fines or damage the institution’s reputation.
The Solution: Institutions need to stay up-to-date with regulatory changes and make sure that all swap transactions are compliant. This can be done by working with legal and compliance teams who can ensure that all necessary steps are followed.
- Interest Rate Risk
- The Problem: Swaps that are linked to interest rates, such as interest rate swaps, are sensitive to changes in those rates. If rates change unexpectedly, the institution could end up in a less favorable position.
The Solution: Financial institutions can use market predictions and data to understand better how interest rates might move. They should also diversify their swap agreements to reduce dependency on interest rate changes.
- Reputational Risk
- The Problem: If swaps are poorly executed or lead to financial losses, it can damage an institution’s reputation. A tarnished reputation can result in a loss of trust from clients and business partners.
The Solution: To protect their reputation, institutions should make sure that swaps are executed properly and with careful planning. Transparency with clients and partners can also help maintain trust.
Dealing with financial complexity and risk management can be overwhelming, especially when you need quick access to funds. Understanding swaps or managing through regulations can add to the stress. Pocketly offers a straightforward solution with its simple, transparent loan process. Get quick access to funds, flexible repayment options, and no complicated paperwork.
Pocketly: Your Flexible Solution to Financial Management
For businesses looking to manage cash flow or individuals needing financial assistance without the complexities of traditional financial instruments like swaps, Pocketly offers a hassle-free solution. Whether you're looking to cover unexpected expenses or require a quick loan for personal projects, Pocketly simplifies the lending process with a fast, transparent, and flexible approach.
- No Guarantor or Collateral Required: Access funds quickly with minimal documentation.
- Flexible Loan Amounts: Borrow between ₹1,000 and ₹25,000, tailored to your specific needs.
- Quick Loan Disbursal: Get your loan approved and disbursed in minutes.
- Repayment Flexibility: Choose repayment options that fit your financial situation.
- Interest Rate: Starting from 2% per month.
- Processing Fee: 1-8% of the loan amount, depending on the loan type and amount.
With Pocketly, you can avoid the complexity and risk of swaps while still achieving your financial goals. Start managing your finances more efficiently by contacting us today.
Also, read our guide on Understanding the Meaning, Types, and Features of Collateral Loans
Conclusion
Managing the world of swaps and their complexities can be challenging, especially for financial institutions. While swaps serve as powerful tools to hedge risks and manage finances, they also come with a set of risks that require careful management. The key to utilizing swaps effectively lies in understanding their nuances, weighing the pros and cons, and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks. Financial institutions that are proactive in risk management strategies can maximize the benefits of swaps while mitigating potential drawbacks.
However, for individuals and businesses seeking a more direct and flexible solution to their financial needs, without the complexities of swaps, Pocketly offers a simplified approach. Download Pocketly Today on Android or iOS and experience an easy, transparent loan process designed to fit your needs. Take control of your finances today with Pocketly.
FAQs
What are the main risks associated with swaps for financial institutions?
Swaps come with risks like counterparty risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and regulatory challenges. Institutions must carefully assess counterparties, monitor market movements, and ensure compliance with regulations to minimize potential losses.
How do swaps help financial institutions manage risks?
Swaps enable financial institutions to hedge against fluctuations in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and commodity prices, thereby stabilizing their financial positions and mitigating risk exposure.
Can swaps be used for purposes other than risk management?
Yes, swaps can also be used for speculation, to gain exposure to different financial markets, or to optimize a financial institution's balance sheet and capital structure.
What steps should financial institutions take to minimize risks in swaps?
Institutions should conduct thorough market analysis, ensure robust risk management frameworks, and assess counterparty creditworthiness. Regular monitoring of swap positions and adherence to compliance standards is also essential.
How does Pocketly offer a simpler financial solution compared to swaps?
Pocketly provides quick, flexible loan solutions with minimal documentation, making it easier for individuals and businesses to access funds without the complexities or risks associated with swaps.