Student loans can accumulate interest quickly, making it difficult to manage the amount owed. Each month, your loan balance increases due to interest, and over time, this can lead to paying back much more than the original loan. The challenge lies in understanding how interest works and how it impacts your repayments, especially when dealing with different loan types and rates.
In this blog, we will explain how student loan interest rates are calculated, the factors that contribute to increasing your debt, and ways to minimise the interest you pay.
Key Takeaways
- Interest Calculation is Key: Understanding how student loan interest is calculated (simple vs. compound) can help you make informed decisions and manage repayments more effectively.
- Compounding Can Add Up: With compound interest, interest accumulates on both the principal and the interest, increasing the total amount you owe over time.
- Paying Extra Helps: Paying more than the minimum or making biweekly payments can reduce your loan balance faster and lower the overall interest you pay.
- Loan Type Matters: Subsidized loans help reduce interest costs since the government covers the interest during study periods, while unsubsidized loans start accruing interest immediately.
- Amortization Reduces Principal: Over time, student loan amortization means more of your monthly payment goes toward the principal, reducing the interest burden in the long run.
Understanding Student Loan Interest
Student loan interest is the cost you pay for borrowing money to fund your education. It’s typically calculated as a percentage of the loan amount, known as the interest rate. Interest can be either fixed, staying the same throughout the loan period, or floating interest, changing over time based on market conditions.
The interest begins accumulating as soon as the loan is disbursed, even if you’re still in school/college. The longer it takes to repay the loan, the more interest it can accumulate, thereby increasing the total amount you owe to the lender.
There are some key terms that you should know about student loan interest:
- Principal: The original loan amount you borrowed
- Interest Rate: The annual percentage charged for borrowing (expressed as APR)
- Daily Interest Rate: Annual rate divided by 365 days
- Interest Accrual: How interest builds up over time
While grasping these fundamental concepts is essential, the real challenge comes when you need to determine exactly how much interest you'll pay over time. Here's how you can calculate your student loan interest step by step.
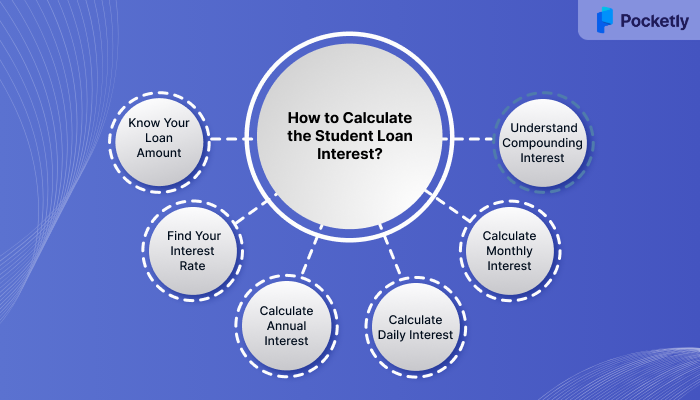
How to Calculate the Student Loan Interest?
Calculating student loan interest can seem complicated, but it's fairly straightforward once you break it down. Here’s a simple, step-by-step process to help you understand how to calculate the interest on your student loan:
Step 1: Know Your Loan Amount
Start by finding out the total amount of money you borrowed.
- For example, if you borrowed ₹1,00,000, that’s your principal.
Step 2: Find Your Interest Rate
Your loan agreement will include an interest rate, typically expressed as a percentage.
- For example, if your interest rate is 10%, this is the rate you will use to calculate the interest.
Step 3: Calculate Annual Interest
To calculate the interest for one year, use this formula:
Interest = Principal × Interest Rate
- For example: If your principal is ₹1,00,000 and your interest rate is 10%, the interest for one year would be: ₹1,00,000 × 10% = ₹10,000
Step 4: Calculate Daily Interest
To calculate daily interest, divide your annual interest by the number of days in a year (365 days).
- For example: Daily Interest = ₹10,000 ÷ 365 = ₹27.40
This means your loan will accumulate ₹27.40 in interest every day
Step 5: Calculate Monthly Interest
To find the monthly interest, you can simply multiply the daily interest by the number of days in the month. For a month with 30 days:
- For example: Monthly Interest = ₹27.40 × 30 = ₹822
So, the interest for one month would be ₹822.
Step 6: Understand Compounding Interest
Many student loans use compound interest, meaning the interest is added to the principal, and you end up paying interest on the accumulated interest, also called “interest accrued”.
To calculate this, interest is added to the loan balance periodically (often monthly or yearly). The more often interest compounds, the more you will owe over time.
- For Example:
If you have a ₹1,00,000 loan with a 10% annual interest rate that compounds monthly, the monthly interest rate is 0.8333% (10% ÷ 12).
- Month 1: Interest for the first month: ₹1,00,000 × 0.8333% = ₹833.33
- Month 2: The new balance is ₹1,00,833.33. So the Interest for the second month: ₹1,00,833.33 × 0.8333% = ₹840.28
As interest is added to the loan each month, you pay interest on the growing balance, causing the loan to increase more quickly.
If you need quick financial assistance to cover educational expenses or unexpected costs, Pocketly offers fast, instant personal loans for students in India, ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000 with an interest rate starting at 2% per month.
What are the Factors Influencing Interest Cost?
When taking out a student loan or any type of loan, understanding the factors that influence interest costs is key to managing your finances. These factors will affect how much you will pay in interest and shape the overall cost of your loan over its lifetime.
Let’s dive into why each of these factors has a significant impact on your interest cost:
Simple vs. Compound Interest
With simple interest, the interest is calculated only on the principal balance, meaning you’ll pay less interest overall. On the other hand, compound interest can cause the amount owed to grow much faster, as interest is charged not only on the principal but also on any accumulated interest.
Here are other key differences:
| Aspect | Simple Interest | Compound Interest |
| Formula | SI = (P × R × T) ÷ 100 | CI = P(1 + r/n)^(nt) - P |
| Growth Pattern | Linear growth with a constant rate. | Exponential growth with an accelerating rate. |
| Interest on Interest | No, interest is not earned on previous interest. | Yes, interest is earned on both principal and interest. |
| Principal Amount | Remains constant throughout the term. | Increases with each compounding period. |
| Return Potential | Lower returns over time. | Higher returns over time. |
| Calculation Method | Straightforward multiplication. | Involves complex calculations with compounding. |
| Compounding Frequency | Not applicable. | Can compound daily, monthly, quarterly, or annually. |
| Loan Cost | Lower cost for borrowers. | Higher cost for borrowers due to compounding. |
| Common Applications | Personal loans, short-term deposits, auto loans. | Savings accounts, credit cards, investments, mutual funds. |
Must Read: Top 30 Instant Loan Apps for Students in India
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates
A fixed interest rate gives you the advantage of stability, ensuring that your monthly payments remain the same, regardless of market conditions. However, it might be set higher than a variable rate initially.
In contrast, variable rates start lower but can increase over time, leading to higher interest costs, in periods of economic growth when market rates rise.
Here are other key differences:
| Aspect | Fixed Interest Rate | Variable Interest Rate |
| Rate Stability | Completely stable, no fluctuations. | Constantly changes based on market rates like prime or repo rates. |
| Monthly Payments | Same amount every month. | Payments fluctuate with rate changes. |
| Market Influence | Unaffected by market changes once set. | Highly influenced by market trends and economic factors. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to predictability. | Higher risk due to unpredictable payment amounts. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility; terms are fixed. | More flexibility can benefit from rate drops. |
| Prepayment Options | May have penalties for early repayment. | No prepayment penalties. |
| Economic Protection | Protected from rising interest rates. | Vulnerable to interest rate increases. |
Subsidized vs. Unsubsidized Loans
With subsidized loans, the government covers the interest while you’re in school, so your loan balance doesn’t grow during that period. In contrast, unsubsidized loans begin accruing interest as soon as you take them, meaning the loan balance increases during your time in school, adding more to the total amount you’ll need to repay later.
The financial burden of unsubsidized loans can be heavier due to this early interest accumulation.
Here are other key differences:
| Aspect | Subsidized Loans | Unsubsidized Loans |
| Financial Need Requirement | Must show financial need through FAFSA. | No financial need requirement. |
| Interest Payment During School | Government pays interest. | Borrower pays interest, or it is added to the loan. |
| Available to Student Types | Only undergraduate students. | Undergraduate, graduate, and professional students. |
| Maximum Time Limit | 150% of program length (e.g., 6 years for a 4-year UG program). | No set time limit. |
| Interest Rates | 6.53% for 2024-25 (same as unsubsidized for undergraduates). | 6.53% for undergraduates, 8.08% for graduate/professional |
| Interest Accrued | Does not accrue during covered periods. | Accrues immediately upon disbursement. |
| Total Cost | Lower cost due to government interest subsidy. | Higher cost due to continuous interest accumulation. |
Understanding these factors gives you insight into how your loan costs are determined, but there's another crucial concept that affects your repayment journey from start to finish.
What is Student Loan Amortization?
Student loan amortization is the process of repaying your loan over time through regular, fixed payments. Each payment consists of 2 parts: the interest on the loan and the repayment of the principal.
In the early stages, a larger portion of your payment goes toward interest, but as the principal decreases, more of your payment reduces the actual loan amount.
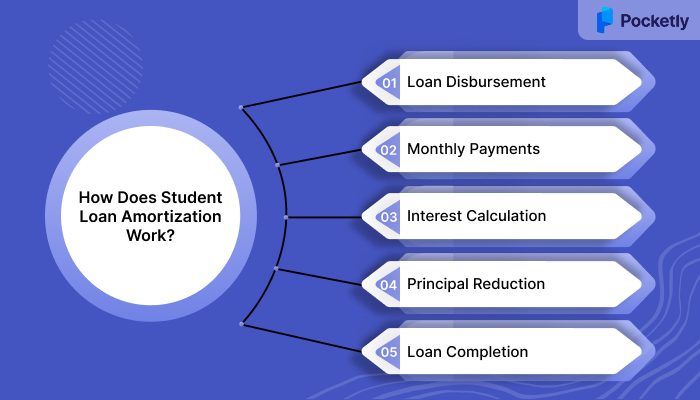
How Does Student Loan Amortization Work?
- Loan Disbursement: After receiving your loan, the total borrowed amount becomes the principal balance.
- Monthly Payments: Every month, you make a fixed payment, which is split between the interest and the principal.
- Interest Calculation: Interest is charged on the remaining principal balance, meaning that as you pay down the loan, the interest charged each month gradually decreases.
- Principal Reduction: As the interest decreases, a larger portion of your monthly payment goes toward paying off the principal.
- Loan Completion: This process continues until the full loan amount is paid off.
Example: Let’s say you take a ₹30,00,000 student loan with a 7% annual interest rate, repaid over 10 years. Your monthly payment would be approximately ₹34,800.
In the first month, ₹17,400 (₹30,00,000 × 7% ÷ 12 ) would go toward the interest, and ₹17,400 would reduce the principal.
By the end of the term, the interest portion of your monthly payment would decrease to around ₹2,400, with ₹32,400 applied to the principal. The total interest paid over 10 years would be approximately ₹4,85,000.
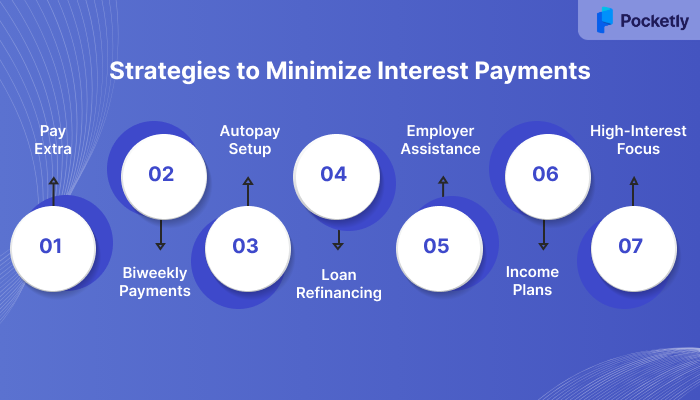
What are the Key Strategies to Minimize Interest Payments?
Managing student loan interest is crucial for reducing the overall amount you’ll repay over time. By applying a few smart strategies, you can lower the interest burden and pay off your loan faster. Let’s take a look:
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Paying extra each month reduces the principal faster, which lowers the interest accrued over time. Even small additional payments can make a difference in the total interest paid.
- Make Biweekly Payments: Instead of monthly payments, pay half of it every 2 weeks. This results in 26 half-payments per year, which is the equivalent of 13 full payments, reducing the loan balance and interest faster.
- Set Up Autopay: Many lenders offer a discount on interest rates (usually 0.25%) for setting up automatic payments. Autopay also ensures timely payments, preventing late fees and negative impacts on your credit score.
- Refinance Your Loans: If you have a good credit score and an income, refinancing your loans can help you secure a lower interest rate, lowering both monthly payments and the total interest paid over time.
- Take Advantage of Employer Repayment Assistance: This assistance for student loan repayment can help you pay off your loan faster without additional financial strain.
- Consider Income-Driven Repayment Plans: If monthly payments are unaffordable, income-driven repayment plans adjust your payments based on your income. These plans may also offer loan forgiveness after a set number of years.
- Target High-Interest Loans First: By focusing on clearing off loans with the highest interest rates first, you minimise the total interest paid. This is the debt avalanche method, as it reduces the overall cost of your loan.
Implementing these strategies requires commitment and planning, but sometimes you need immediate financial support while working toward your long-term loan management goals.
Why Choose Pocketly for Your Student Loan Needs?
Pocketly is a digital lending platform designed to provide quick and hassle-free financial assistance to students. Here’s why it’s a great option for managing your student loan needs:
- Fast Application: Simple, online application with minimal documentation.
- Flexible Personal Loan Amounts: Borrow from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000 based on your needs.
- Quick Approval and Disbursal: Get approved and receive funds within 24 hours.
- Affordable Interest Rates: Competitive rates starting at 2% per month.
- Low processing fees ranging from 1% to 8% of the loan amount, depending on the loan type.
- Convenient Repayment: Easy, flexible loan repayment schedule options with auto-debit.
Conclusion
Managing student loan interest can feel overwhelming, but understanding how interest is calculated and applying smart strategies can significantly reduce the financial burden. By focusing on reducing the interest accrued and making timely payments, you can minimise the total amount you repay.
Whether it’s through paying extra, refinancing, or taking advantage of employer assistance, there are numerous ways to manage and reduce your student loan costs.
For students and salaried professionals in need of quick financial assistance, Pocketly is a digital lending platform that offers fast loan approvals, often within minutes. Download Pocketly today on Android or iOS and experience financial solutions at your fingertips.
FAQ’s
1. What are the tips for paying less interest on student loans?
To pay less interest, consider making extra payments toward the principal whenever possible. Refinancing your loan for a lower interest rate or enrolling in automatic payments (which sometimes offer discounts) can also help reduce the interest burden.
2. Can I reduce my education loan EMI amount?
Yes, you can reduce EMI by opting for a longer repayment term. However, this will lower your monthly payments while increasing the total interest paid over time. Alternatively, refinancing might help reduce your EMI if you qualify for better terms.
3. How to get a 0% interest education loan?
Getting a 0% interest education loan is rare, but some government schemes or special institutional loans may offer it. It's best to research specific programs that provide interest-free loans based on financial need or educational course.
4. What if I don't pay my student education loan?
Not paying your student loan can harm your credit score, incur late fees, and lead to legal action. It's important to contact your lender to explore deferment options or repayment plans if you're struggling financially.
5. Are hostel fees included in student education loans?
Yes, most education loans cover hostel fees as part of the overall cost of education, as long as you can provide proof of the expenses.