Digital wallets sit at the centre of everyday payments in India, covering bill payments, metro rides, subscriptions, and quick store checkouts. Their use is only accelerating. The RBI’s Digital Payments Index touched 493.22 in March 2025, up from 465.33 in September 2024, reflecting not just rising adoption but also stronger digital infrastructure across the country. With more than 208 billion digital transactions recorded over the past year, UPI is clearly leading the way, and wallets remain a vital part of this growth story, offering rewards, small-ticket convenience, and quick settlements.
In this blog, we’ll look at the best digital wallets in India today, how they differ from UPI, the features that set them apart, and which options suit different needs.
Key Takeaways
- Wallets are diverse: Closed, semi-closed, open, UPI Lite, device-based, and even crypto wallets exist, each with different usage limits and acceptance levels.
- User scale is massive: PhonePe and Google Pay together process over 80% of UPI transactions, while Paytm, Amazon Pay, and MobiKwik still serve millions across varied segments.
- Technology drives trust: Tokenisation, encryption, QR protocols, and NFC are core to how wallets ensure fast yet secure transactions.
- Benefits vs limits: While wallets offer speed, rewards, and easy tracking, they also come with caps, internet dependence, and regulatory risks.
- Future is smarter: AI-led fraud detection, offline UPI Lite X, credit-on-UPI, and India’s digital rupee will reshape how wallets are used in the next few years.
What is a Digital Wallet?
A digital wallet is a mobile or web-based application that securely stores your payment details, such as debit or credit cards, UPI IDs, and sometimes loyalty points or passes. It lets you pay instantly at shops, online platforms, or within apps without needing physical cash or cards. Many wallets also support bill payments, ticket bookings, and quick money transfers, making them a convenient all-in-one option for everyday transactions.
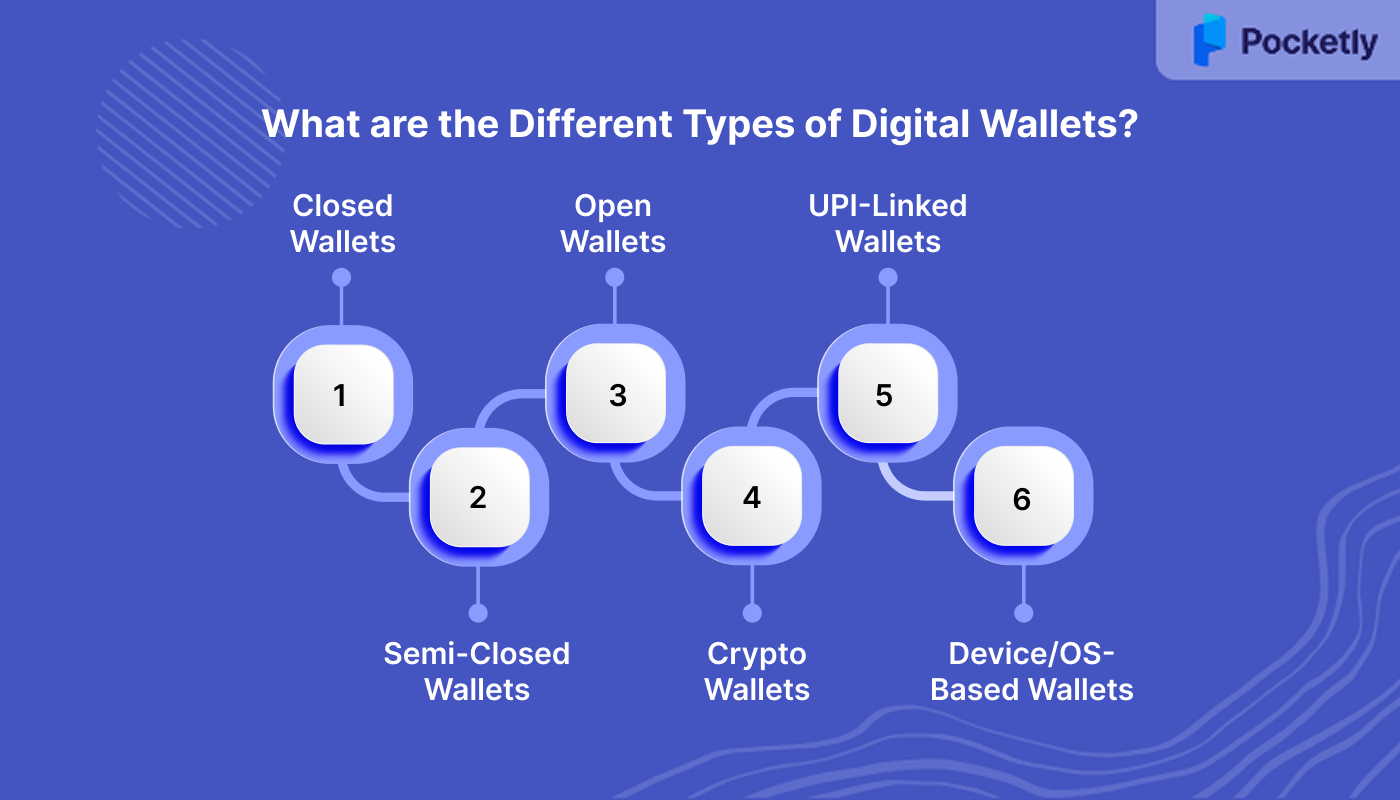
What are the Different Types of Digital Wallets?
Digital wallets come in different forms, each designed for specific uses. Some are limited to one brand, while others work across merchants or link with banks. Knowing these types makes it easier to pick the wallet that fits your daily spending habits.
1. Closed Wallets
These are issued by a specific company and can only be used for transactions with that company. Users can load money into the wallet, but cannot withdraw it as cash. Refunds for cancellations or returns are usually credited back into the same wallet.
Example: Amazon Pay Wallet, Ola Money.
2. Semi-Closed Wallets
These wallets allow transactions with a range of merchants and service providers who have a contract with the wallet issuer. Money can be loaded and used for payments, but cash withdrawals are not permitted. They are popular for online shopping, bill payments, and travel bookings.
Example: Paytm Wallet, PhonePe Wallet, Mobikwik.
3. Open Wallets
Issued by banks or institutions partnered with banks, open wallets can be used for purchases at any merchant that accepts card payments, both online and offline. Users can also withdraw cash from ATMs and transfer funds to bank accounts.
Example: ICICI Pockets, HDFC PayZapp.
4. Crypto Wallets
While still a niche in India due to regulatory uncertainty, crypto wallets allow users to store and transact in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. They provide private keys and secure storage, often with features like two-factor authentication.
Example: WazirX Wallet, CoinDCX Wallet.
5. UPI-Linked Wallets (UPI Lite)
These are lightweight digital wallets integrated with UPI for small-ticket payments. They allow users to top up a limited amount (e.g., ₹2,000–₹4,000) and make instant, tap-to-pay or scan-based transactions without relying on bank servers each time. Ideal for quick daily spends.
Example: Paytm UPI Lite, PhonePe UPI Lite.
6. Device/OS-Based Wallets
These are digital wallets integrated with smartphones or operating systems. They support contactless payments via NFC, tokenised card storage, and sometimes transit passes. Adoption in India is rising with metro systems, airlines, and retail tie-ups.
Example: Google Wallet, Apple Wallet, Samsung Pay.
Also Read: Digital Wallet Benefits and Features Explained
Among these categories, certain wallets have emerged as clear leaders in the Indian market. Their dominance stems from strategic positioning, user trust, and the ability to scale across diverse payment scenarios, from street vendors to premium retail outlets.
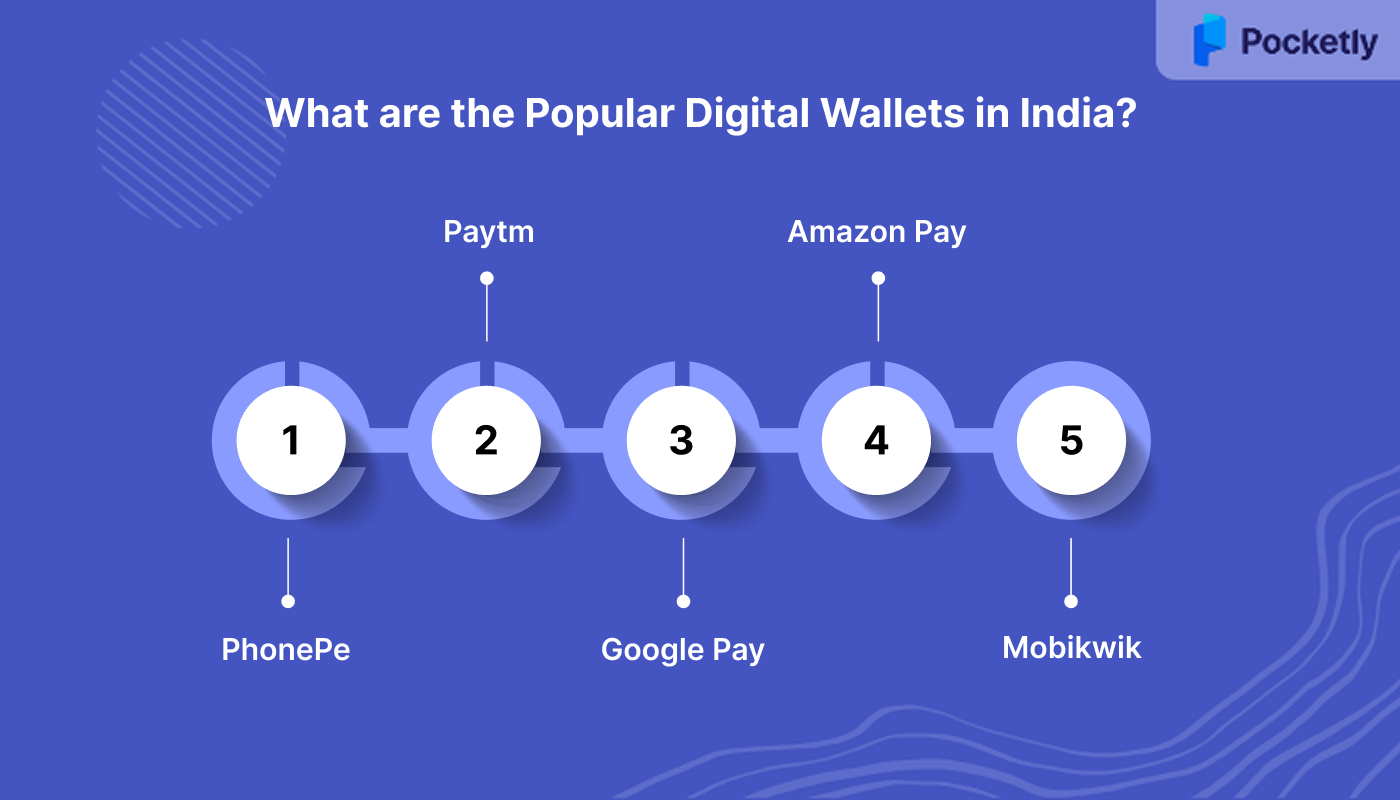
What are the Popular Digital Wallets in India?
Each wallet has its own story, some backed by global tech firms, others homegrown with deep local reach. Knowing the background, scale, and where these wallets are most used helps you make a smarter choice.
Instead of just focusing on features, looking at their user base, market presence, and trust factor gives a clearer picture of why they’re popular and how they might suit your everyday payments.
1. PhonePe
PhonePe was founded in December 2015 by Sameer Nigam, Rahul Chari, and Burzin Engineer. It launched its UPI-based app in August 2016 and was later acquired by Flipkart in early 2016. As of March 2025, it has crossed 600 million registered users, supported by a presence across over 40 million merchants, and processes more than 330 million transactions daily with an annualised payment volume exceeding ₹150 lakh crore.
The features are:
- Works seamlessly for both everyday payments and financial services like mutual funds, insurance, and gold investments.
- The multi-lingual interface supports 11 Indian languages.
- Strong merchant acceptance across both urban and rural areas.
- Features like QR payments, Fastag recharge, and integrated offers.
2. Paytm
Paytm traces its origins back to 2010, when Vijay Shekhar Sharma founded One97 Communications in Noida. The Paytm Wallet emerged soon after and quickly became one of India’s most recognisable digital payment brands. In Q2 2025 alone, the wallet handled transactions worth around ₹4.4 trillion, reaching over 350 million active users.
The features are:
- Offers wallet, UPI, and payment gateway modes—great for flexibility.
- Includes services like Paytm Postpaid (“buy now, pay later”), ticket booking, and bill payments.
- Widespread QR acceptance at kirana shops and neighbourhood stores.
- Loyalty-driven perks and discounts, especially during festive seasons.
3. Google Pay
Google Pay (initially launched as Tez) made its India debut in September 2017, built on NPCI’s UPI framework to simplify digital payments across the country. It was rebranded as Google Pay in August 2018 to align with the broader global payment brand.
While global figures place Google Pay at around 820 million active users in 2025, India alone accounts for approximately 62% of this, making it the platform’s single largest market. That equates to roughly 510 million users in India.
It’s especially popular in urban centres, where Android adoption is high; about 75% of smartphone users in major Indian cities have Google Pay installed. The app is accepted by a vast majority of online retailers, and 88% of e‑commerce merchants in India support Google Pay at checkout.
The features are:
- Clean and intuitive interface, popular with first-time digital payment users.
- Integrated rewards via scratch cards and cashback offers.
- AutoPay feature for recurring bills and subscriptions.
- Trusted due to its link with the Google ecosystem.
4. Amazon Pay
Amazon Pay’s journey began earlier; it was launched in August 2007 as an online payments solution leveraging users' Amazon account details for seamless checkouts on partner sites.
In India specifically, Amazon Pay has seen steady growth: as of August 2024, the platform had crossed 100 million registered users since its launch in India in 2019. While not as dominant as UPI-powered wallets, it retains a meaningful presence. NPCI data shows that in May 2024, Amazon Pay handled 68 million UPI transactions worth ₹7,419 crore, capturing about 0.9% of the total UPI volume.
The features are:
- Smooth integration with Amazon shopping, Prime membership perks, and order refunds.
- Accepts wallet payments across groceries, offline stores, and third-party services.
- Regular cashback and promotional offers enhance the value of purchases.
5. Mobikwik
Founded in 2009 by Bipin Preet Singh and Upasana Taku, MobiKwik started as a website-based wallet and secured RBI approval for a semi-closed wallet in 2013. Headquartered in Gurugram, it has steadily built its position as one of India’s leading wallet providers.
As of mid-2024, the platform had over 161 million registered users and connected with around 4.26 million merchants across India, making it the third-largest wallet player by user base. About 30 million people use it monthly, with a growing share coming from Tier II and Tier III cities, showing its strong presence outside major metros.
MobiKwik’s valuation crossed $1.2 billion in 2025, supported by a $70 million funding round aimed at expanding lending and payment services before its IPO. Its steady growth and regional reach highlight its relevance in India’s digital payment ecosystem.
The features are:
- Strong in offering short-term loans and BNPL services (MobiKwik Xtra).
- Provides basic payments, bill pay, and recharge features.
- Lightweight version (MobiKwik Lite) works even in low-internet zones.
- Good choice for users seeking flexibility with credit options.
Also Read: Recent Financial Services Trends of 2025
Behind these user-friendly interfaces and instant transactions lies a sophisticated technical infrastructure. Understanding the mechanics of how these platforms actually process your payments reveals why they've become so reliable and secure in just a few short years.
How Do Digital Wallets Work?
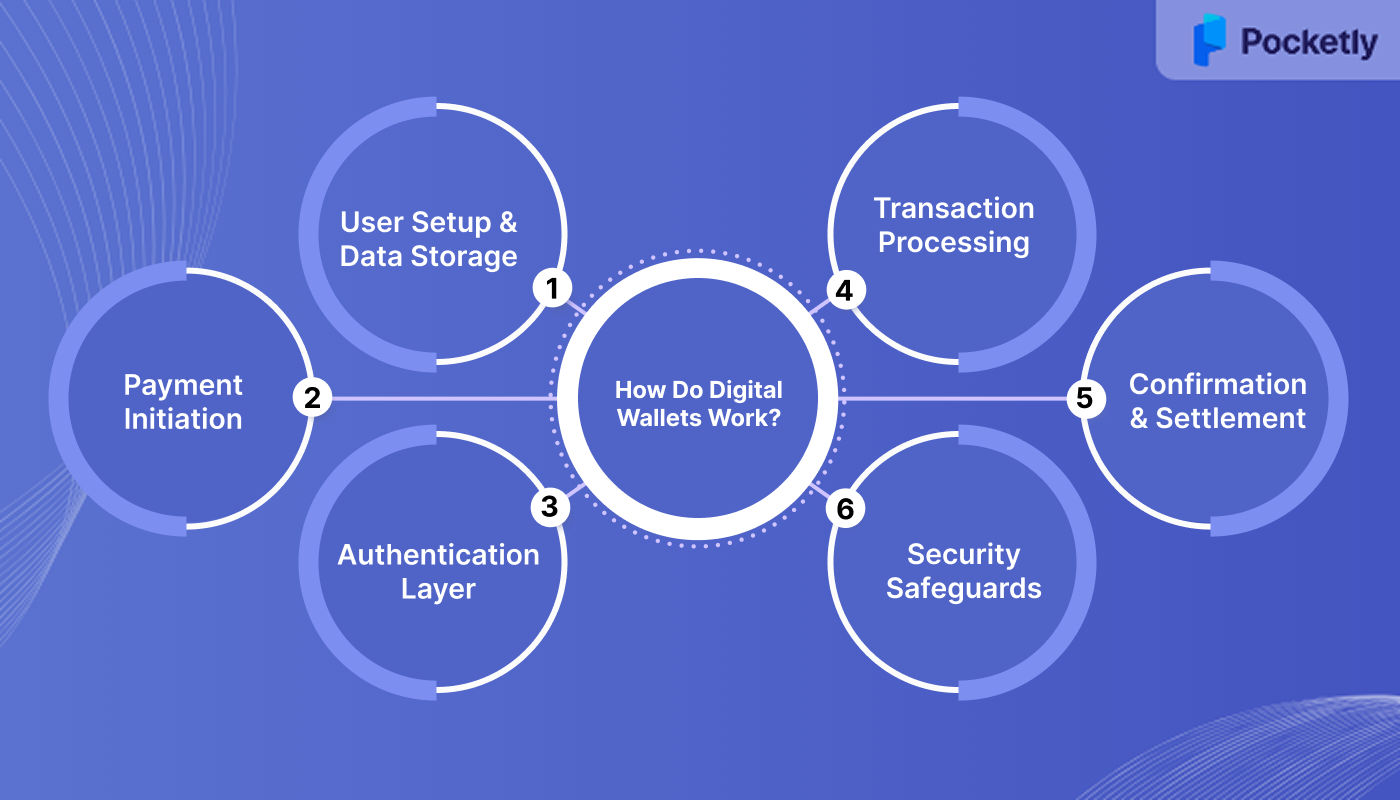
Digital wallets are not just apps but secure systems built on encryption, tokenisation, and regulated payment infrastructure. Here’s how they function step by step:
1. User Setup and Data Storage
When you first add a debit card, credit card, or bank account, the wallet doesn’t store your raw details. Instead, it either saves them in a secure element on your device (like Google Wallet or Apple Wallet) or in encrypted servers maintained by the provider (like Paytm or PhonePe). In India, RBI’s card tokenisation mandate ensures that your actual card number is never exposed.
2. Payment Initiation
Once set up, payments can be triggered at offline or online merchants. At stores, you either scan a QR code to tap your phone at the point-of-sale terminal using NFC (Near Field Communication). Online, wallets connect with merchant websites or apps through API integrations that transmit encrypted requests to payment gateways.
3. Authentication Layer
Before the payment goes through, the wallet requires verification. This step prevents unauthorised use of your funds. Depending on the wallet, this could involve entering a UPI PIN, a biometric check like a fingerprint or face scan, or an OTP sent to your phone. Many wallets follow two-factor authentication (2FA), which combines two different security checks for added safety.
4. Transaction Processing
Once authenticated, the wallet generates a payment request and sends it to the bank or card network. In case of UPI wallets, this request flows through the NPCI (National Payments Corporation of India), which routes it between the payer’s and payee’s banks. For card-linked wallets, the encrypted card token is validated by Visa, Mastercard, or RuPay.
5. Confirmation and Settlement
After checking the balance and transaction limits, the bank approves the payment. A confirmation is sent back instantly to the wallet and merchant, so the user sees a success screen. In the background, actual fund settlement between banks happens later in regulated clearing cycles, but to the customer, the payment feels instant.
6. Security Safeguards Throughout
Every stage of the wallet’s functioning is guarded by multiple technologies. The use of dynamic QR codes, NFC encryption, and PCI-DSS compliance ensures merchants never see your full card details. Combined with RBI’s regulatory framework and real-time monitoring by providers, wallets maintain both speed and security.
From streamlining your morning coffee purchase to securing your online shopping, digital wallets deliver benefits that extend far beyond simple payment processing.
Benefits of Using Digital Wallets
Digital wallets have grown popular not just because they’re convenient but also because they combine speed, security, and added value in everyday payments. They simplify how people manage money and offer more than just a way to pay.
- Convenience: Pay instantly without carrying cash or cards.
- Speed: Quick checkouts online and offline with QR or tap-to-pay.
- Security: Tokenisation, encryption, and biometrics keep payments safe.
- Tracking: Built-in records help you monitor expenses easily.
- Rewards & Offers: Many wallets give cashback, discounts, or loyalty points.
- Wide Acceptance: Used across e-commerce, utility bills, travel, and local stores.
Despite these compelling advantages, digital wallets aren't perfect solutions for every payment scenario. Certain constraints and dependencies can affect their reliability, especially in specific situations or regions where infrastructure challenges persist.
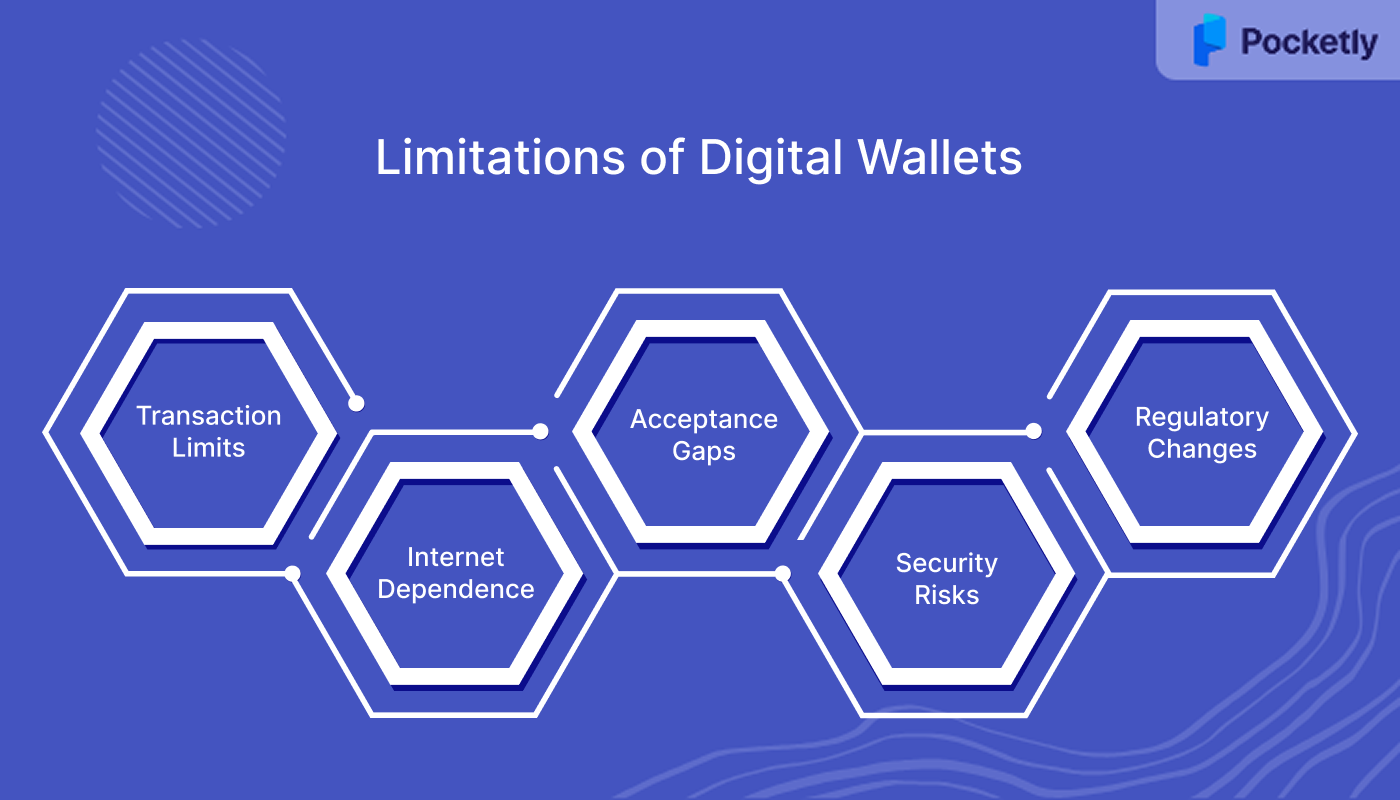
Limitations of Digital Wallets
While digital wallets bring convenience, they also come with a few restrictions that readers should be aware of. Understanding these helps in setting the right expectations before relying on them for all payments.
- Transaction Limits: Most wallets have daily or monthly caps on loading money and spending.
- Internet Dependence: Payments require stable connectivity, making them less reliable in low-network areas.
- Acceptance Gaps: Some smaller merchants or service providers may still prefer cash or UPI directly.
- Security Risks: Although secure, phishing attempts and fake QR codes can trick users into fraudulent payments.
- Regulatory Changes: RBI guidelines or compliance issues can affect services, such as restrictions placed on wallet top-ups.
Given these trade-offs between benefits and limitations, selecting the right wallet becomes crucial. Your choice should align with your specific needs, spending patterns, and priorities rather than simply following popular recommendations.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Digital Wallet
Choosing a digital wallet isn’t just about the prettiest interface or fastest checkout. What really matters is how well it aligns with your habits, priorities, and the safety it offers. Drawing from academic studies and practical guides, here are the key factors you should keep in mind:
1. Security and Privacy: Safety ranks among the top reasons people choose a wallet. Strong encryption, tokenisation, secure storage, and multi-factor authentication protect your sensitive data and reduce the risk of fraud or compromise.
2. Trust and Reliability: Trust, not just usability, drives long-term use. A wallet backed by established financial bodies, with transparent policies and reliable uptime, earns confidence and encourages continued use.
3. Convenience and Usability: Ease-of-use matters. A wallet that’s intuitive, integrates across your devices (phones, apps, retail checkouts), and supports your regular payment modes makes it more likely you'll stick with it.
4. Offers and Rewards: For many users, perks such as cashback, discounts, or loyalty rewards make a wallet more appealing. These add tangible value, especially when they align with your frequent purchases.
5. Adoption & Acceptance: Even the safest wallet won't help if merchants don't accept it. Look for wide mall, app, and local-store support and, if relevant, peer usage in your social circle.
6. Cost and Fees: Wallets vary in fee structures; some charge for top-up or transfers, others are free. It's wise to compare total costs, including hidden charges and conditions, before you commit.
7. Customer Support & Integration: When things go wrong, responsive customer support can be a lifesaver. Also consider if the wallet integrates smoothly with other platforms or services you use, e.g., shopping apps or expense trackers.
8. Peer Influence & Social Proof: If your friends or family use a certain wallet, you're more likely to trust and adopt it yourself. Social recommendations still influence choices a lot, even with tech.
The digital payments industry is experiencing rapid transformation driven by emerging technologies, regulatory shifts, and changing user expectations that will reshape how we think about digital money.
Future Outlook and Challenges for Digital Wallets in India
India’s wallets are moving from “just pay” to smarter, safer, and more open money tools. Three big currents are shaping the next few years: AI-driven security, always-on/low-connectivity payments, and new rails such as credit-on-UPI and the digital rupee.
- AI everywhere: fraud defence, biometrics, and real-time screening: The RBI proposed a Digital Payments Intelligence Platform and has piloted MuleHunter.AI to spot mule accounts; NPCI also runs AI/ML-based fraud-risk monitoring for members. Biometric checks for UPI (moving beyond PIN) are being readied.
- Data law is getting stricter: The DPDP Act 2023 is in force, with rules tightening how personal data is collected in public spaces (e.g., phone numbers at checkout). Wallets must upgrade consent, notices, and privacy controls accordingly.
- KYC and interoperability for PPIs on UPI: Only full-KYC wallets can ride UPI; transactions are pre-approved using existing wallet credentials before hitting UPI rails.
- Market concentration remains a watch item: NPCI has deferred the 30% UPI market-share cap to Dec 2026, effectively extending the runway for the two biggest apps. This affects discoverability for smaller wallets and shapes the partnership strategy.
Amid these broader industry developments, innovative solutions are emerging to address specific user needs that traditional wallets haven't fully solved. One such example is the growing demand for quick, hassle-free credit access integrated within the digital payments ecosystem.
Pocketly: Smarter Short-Term Credit for Everyday Needs
Pocketly is designed for young professionals and students who need quick access to small-ticket personal loans without lengthy paperwork. With simple eligibility, fast approvals, and flexible repayment options, it helps you manage urgent expenses responsibly. Transparent charges and RBI-registered partners ensure safety and trust.
- Instant loans ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000
- Flexible repayment schedules tailored to your cash flow
- Transparent interest rates between 2% per month
- One-time processing fee of 1%-8% of the loan amount.
- 100% digital onboarding with minimal KYC steps
- Direct disbursal to your bank account or UPI ID
Conclusion
Digital wallets now power everyday payments in India. This guide covered what wallets are, their types, the most used brands, and how the tech works. You also saw the key benefits, limits, and what to check before choosing one. We closed with the road ahead, including AI-led security, offline payments, credit on UPI, and the digital rupee. Pick a wallet that matches your spending, device, and comfort with security controls.
Need quick credit for urgent expenses? Pocketly offers instant loans up to ₹25,000 with clear pricing and paperless KYC. Download now on iOS or Android to get started.
FAQs
1. Which digital wallet has no KYC in India?
Currently, no wallet operates without KYC in India. RBI rules mandate at least a minimum KYC for opening a wallet, while full KYC unlocks higher limits and added features.
2. Do I need a PIN for a digital wallet?
Yes, most wallets require some form of authentication. UPI needs a PIN, card-based wallets may use biometrics or phone passcodes, and some transactions use OTPs for extra security.
3. Can I withdraw with my digital wallet?
Only open wallets issued by banks allow cash withdrawal at ATMs. Semi-closed wallets like Paytm or PhonePe can be used for payments, but not for direct cash withdrawal.
4. Can you get cash back using Google Wallet?
In India, Google Wallet only stores cards and passes. Payments and cashback rewards are linked to Google Pay, which offers scratch cards and promotional benefits.
5. What is the 4-hour rule of UPI?
The 4-hour rule is a safety measure applied when you add a new beneficiary. Higher-value transfers are restricted for four hours to reduce fraud risks, though limits vary by bank.