A digital wallet is a powerful financial tool, allowing users to make payments, store credit card details, and even manage loans, all from the convenience of their smartphones. Far beyond simply replacing cash or physical cards, digital wallets provide a secure, efficient way to handle everyday transactions. With the rise of fintech, these wallets are reshaping how we approach personal finance, offering new ways to access funds, track spending, and streamline payments.
In this blog, we’ll examine how digital wallets work, their key features, and why they’ve become important in modern financial management.
Key Takeaways
- Digital Wallets Offer More Than Payments: Beyond just storing payment details, digital wallets provide a secure and efficient way to manage spending, track finances, and access additional financial services like loans.
- Payment Technologies: Digital wallets leverage technologies like NFC, MST, and QR codes to ensure fast, secure transactions both online and in-store.
- Security Features: Tokenization, encryption, and biometric authentication are key technologies that safeguard users' financial data, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Types of Digital Wallets: Digital wallets are categorized into closed, semi-closed, and open wallets, each with varying levels of flexibility and functionality based on user needs.
- Versatile Financial Tool: Digital wallets are not only for payments; they can store credit/debit cards, loyalty cards, digital IDs, cryptocurrency, and even insurance information.
What is a Digital Wallet
An e-wallet, referred to as a digital wallet, is a software-based solution that stores payment information and allows users to make transactions electronically. It securely holds credit card details, debit card information, and even digital currencies, all accessible through a mobile device or computer.
With digital wallets, users can make instant payments, track spending, and access other financial services without the need for physical cards or cash. These wallets use encryption and security protocols to protect sensitive data, making them a convenient and safe alternative for managing day-to-day finances.
What is the Purpose of a Digital Wallet?
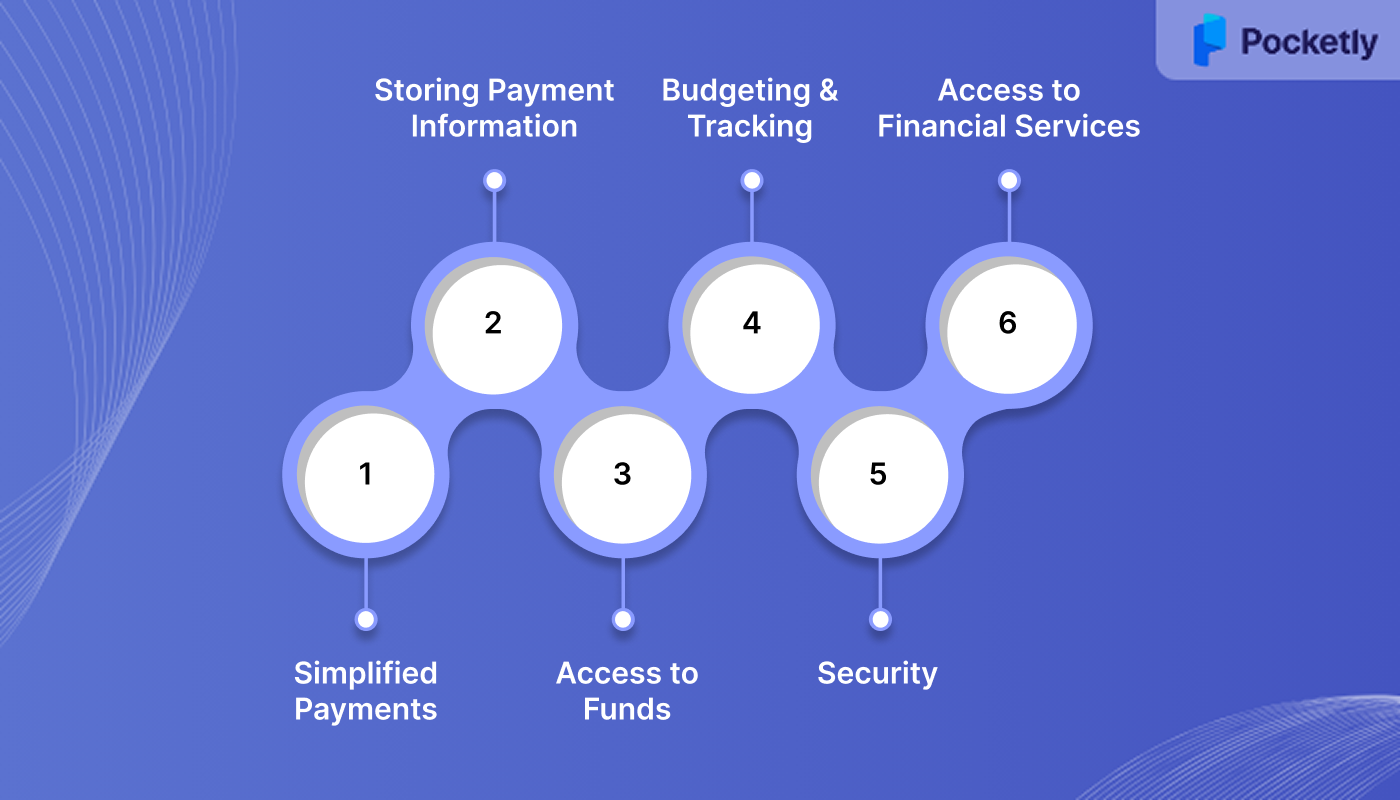
A digital wallet serves as a solution for managing finances, offering users a secure and convenient way to handle payments, store information, and access various financial services. Here’s how it works:
- Simplified Payments: Enables fast, secure transactions without the need for physical cards or cash.
- Storing Payment Information: Stores credit, debit card details, and other payment methods for easy access.
- Access to Funds: Allows users to store and transfer money digitally, making it easier to pay bills, shop, or send money.
- Budgeting and Tracking: Helps track spending patterns, manage finances, and set budgets directly through the wallet app.
- Security: Uses encryption and authentication measures to protect financial data, ensuring safe transactions.
- Access to Financial Services: Integrates with services like loans and digital banking, offering a seamless financial experience.
The functionality of digital wallets extends far beyond basic payment processing. To truly appreciate their versatility, it's essential to examine the diverse range of items these platforms can accommodate.
What Items do Digital Wallets hold?
Digital wallets are versatile tools that can hold a wide range of items, like bank account information, card details, loyalty cards, and more. Below is an overview of the items, along with examples for each category:
| Item | Description | Examples |
| Credit/Debit Cards | Store card details for easy access and payments. | Google Pay (Visa, MasterCard), Apple Pay (American Express, Visa) |
| Bank Account Information | Link bank accounts for direct transfers and payments. | Google Pay (Bank Account Linking), PhonePe (Account Linking for UPI), Paytm Wallet |
| Gift Cards & Loyalty Cards | Digital versions of store or brand gift cards and loyalty memberships. | Amazon Pay (Amazon Gift Cards), Flipkart Gift Cards, Walmart eGift Cards |
| Digital IDs & Documents | Store government-issued IDs, e-tickets, and other essential documents. | Digilocker (Driver's License, Aadhaar card, Marksheets) |
| Cryptocurrency | Store digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc. | Coinbase Wallet, Binance Wallet, Coinomi Wallet |
| Insurance Information | Store digital insurance cards and policies for easy access. | Paytm (Insurance Policies), PhonePe (Health Insurance Digital Cards) |
| Public Transport Cards | Store digital versions of transport cards for easy access to public transit. | Google Pay (Transit passes for metros/buses) |
While the storage capabilities showcase the potential of digital wallets, the real magic happens behind the scenes. The seamless experience users enjoy is the result of sophisticated technological processes working in harmony.
How Digital Wallets Work
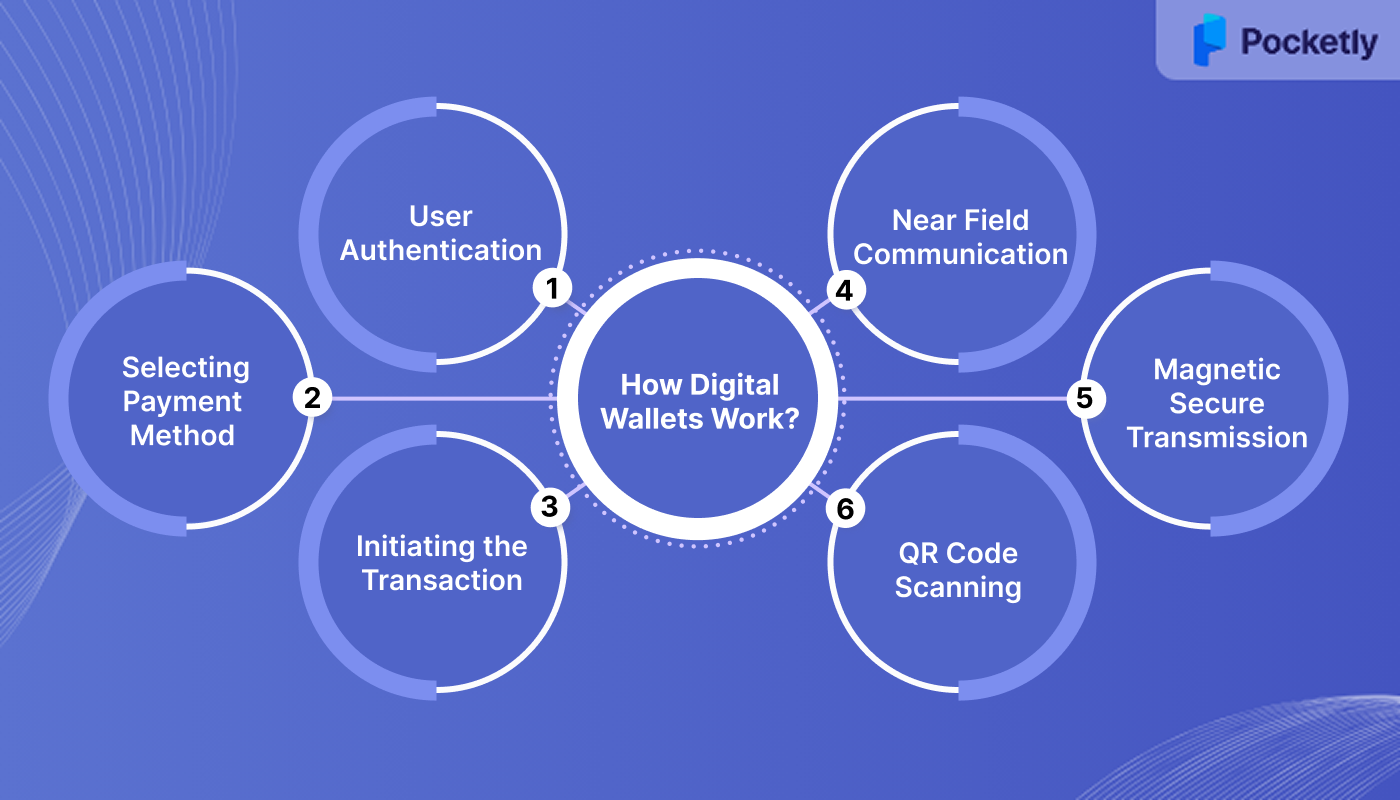
A digital wallet operates using advanced technologies that ensure secure, fast, and convenient transactions. Here’s a look at how these technologies come together to make digital wallets work:
Step 1: User Authentication
Before initiating a transaction, the user unlocks their device using a secure method, such as a PIN, fingerprint, or facial recognition. This step ensures that only authorized individuals can access the digital wallet.
Step 2: Selecting the Payment Method
Once authenticated, the user opens their digital wallet app and selects the preferred payment method, which could be a linked credit or debit card, bank account, or stored balance.
Step 3: Initiating the Transaction
The user proceeds to make a payment at a merchant's point-of-sale (POS) terminal. Depending on the technology supported by both the user's device and the merchant's terminal, one of the following methods is used:
- Near Field Communication (NFC): The user holds their device close to the POS terminal. NFC allows for secure data exchange over short distances (typically less than 4 cm), enabling contactless payments.
- Magnetic Secure Transmission (MST): In terminals without NFC capabilities, this technology emits a magnetic signal that simulates the magnetic stripe of a traditional credit card. This allows the digital wallet to communicate with older POS systems.
- QR Code Scanning: The user scans a QR code displayed by the merchant using their device's camera. The digital wallet app processes the payment by reading the code, which contains the merchant's payment information.
Step 4: Data Transmission and Tokenization
Once the payment method is selected and the transaction is initiated, the digital wallet transmits the payment information to the POS terminal. To enhance security:
- Tokenization: Instead of sending the actual card number, the digital wallet generates a unique token, a one-time code that represents the user's payment information. This token is transmitted to the POS terminal, reducing the risk of sensitive data exposure.
- Encryption: The transmitted data is encrypted, ensuring that even if intercepted, it cannot be read or tampered with.
Step 5: Transaction Authorization
The POS terminal forwards the tokenized payment information to the payment processor, which communicates with the issuing bank to authorize the transaction. This process involves verifying the user's account, checking for sufficient funds, and ensuring there are no fraud alerts.
Step 6: Transaction Completion
Upon successful authorization, the payment processor sends an approval message back to the POS terminal, completing the transaction. The merchant receives the payment, and the user gets a notification confirming the successful payment.
Step 7: Transaction Record and Security Measures
After the transaction, the digital wallet app updates the user's transaction history. To maintain security:
- Biometric Authentication: For subsequent transactions, the wallet may require biometric verification (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition) to authorize payments.
- Remote Locking: If the user's device is lost or stolen, the digital wallet can be locked remotely or wiped to prevent unauthorised access.
The digital wallets enable different service models to emerge, each catering to specific user needs and business requirements. These variations in wallet architecture determine everything from transaction limits to the breadth of services available.
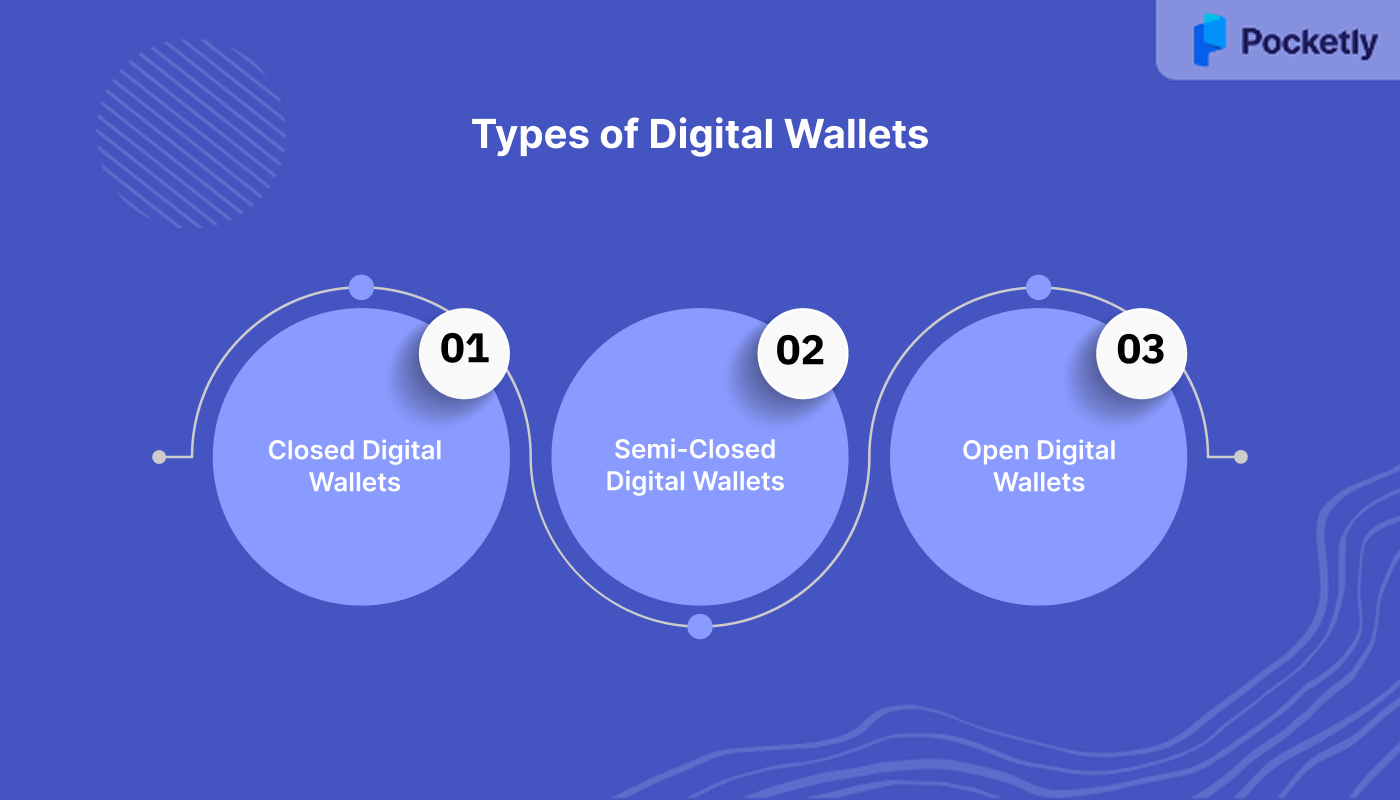
Types of Digital Wallets
Digital wallets come in various forms, each offering different features and levels of functionality. Broadly, they can be categorized into three main types, with several subcategories expanding on these core functions:
1. Closed Digital Wallets
These wallets are issued by specific companies or merchants and can only be used for transactions within their ecosystem. They are typically used for purchasing goods and services from the issuing business (e.g., Amazon Pay, Starbucks Wallet).
2. Semi-Closed Digital Wallets
These kinds of wallets allow users to store funds and do transactions with a wider range of merchants, but do not support withdrawals or redemption of funds (e.g., Paytm, PhonePe).
- Mobile payment wallets are smartphone-based applications that enable users to store funds digitally and make instant payments. These wallets are essential for digital lending platforms as they provide seamless loan disbursement and loan repayment capabilities directly through mobile devices. (e.g., Google Pay, Apple Pay).
3. Open Digital Wallets
The most flexible option, open wallets allow users to make transactions, transfer funds to bank accounts, and use their wallet across a broad range of merchants and services (e.g., Google Pay, Apple Pay). These wallets often support both online and in-store purchases.
- BNPL (Buy Now, Pay Later) Wallets: These wallets are integrated with open wallets to facilitate payments in installments, offering flexible financing options for consumers (e.g., Klarna, Afterpay).
- Credit-Linked Digital Wallets: These wallets allow users to store and manage funds linked to their credit accounts. They are often integrated with open wallets to track and manage credit card or loan repayments (e.g., Paytm Credit, Slice).
- P2P (Peer-to-Peer) Lending Wallets: While typically more specialized, these wallets allow users to lend and borrow directly from one another, often facilitating access to credit in a decentralized manner (e.g., Faircent, Lendbox).
- Business and SME Lending Wallets: These are designed for SME's to access working capital, manage loans, and streamline business-related transactions (e.g., Lendingkart, Capital Float).
The diverse wallet types available today are made possible by an equally diverse technological foundation that works together to ensure security, speed, and reliability across all transaction types.
What are the Technologies Used in Digital Wallets
Digital wallets rely on several key technologies to ensure secure, efficient, and seamless transactions. Here are the primary technologies used in digital wallets:
- Near Field Communication (NFC): A wireless communication technology where user can make contactless payments by simply tapping their mobile device near a POS terminal.
- Magnetic Secure Transmission (MST): Used by some wallets (like Samsung Pay) to mimic the magnetic stripe on a traditional card, enabling compatibility with older POS systems that don't support NFC.
- QR Codes: Used for both in-person and online payments, QR codes allow users to scan or be scanned to make transactions easily and securely.
- Tokenization: This safety feature technology replaces sensitive payment information (like card numbers) with a unique token, ensuring that the actual data isn't exposed during transactions.
- Encryption: Ensures that data transmitted between the wallet and merchant is securely encrypted, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring privacy.
- Biometric Authentication: Utilized for securing access to the wallet and authorizing transactions, including fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice recognition.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Another layer of security where users verify their identity with a second form of authentication (e.g., OTP via SMS or email).
- Cloud Computing: Many digital wallets store data on cloud servers, allowing users to access their wallets across multiple devices while maintaining secure backups.
While the technological sophistication of digital wallets is impressive, the ultimate question for most users remains practical: are they worth adopting? Understanding the real-world implications, both positive and negative, helps paint a complete picture.
What are the Pros and Cons of Using Digital Wallets?
Digital wallets, although they have become a staple in financial management, offer a range of advantages that streamline payments and enhance security. However, like any technology, they come with their own set of challenges.
Below, we’ll explore the key pros and cons of using digital wallets, helping you evaluate whether they align with your financial needs.
Pros of Using Digital Wallets
1. Convenience and Speed: Digital wallets eliminate the need to carry cash or cards. Payments are completed in seconds, either through NFC, QR codes, or direct transfers, making everyday purchases quicker and more efficient.
2. Enhanced Security: Digital wallets use advanced encryption, tokenization, and biometric authentication (fingerprint/face recognition) to protect sensitive data. They reduce the risk of fraud by never storing card details on physical devices.
3. Easy Access to Financial Services: Many digital wallets provide access to a wide range of financial services beyond payments. Users can manage credit, transfer funds, pay bills, access instant personal loans, and track spending all in one place.
4. Rewards and Discounts: Digital wallets often offer rewards programs, cashback, and exclusive discounts. Users can link loyalty cards directly to the wallet and automatically apply offers during purchases.
5. Transaction Tracking and Budgeting: With integrated transaction history, digital wallets allow users to track their spending, categorize expenses, and even set budgets, providing better financial control.
6. Universal Accessibility: Digital wallets make it easy to make payments across borders, with support for multiple currencies. They reduce the hassle of converting currency when traveling internationally.
7. Reduced Risk of Loss: Losing a physical wallet can be stressful, but with digital wallets, users can easily lock, disable, or remotely wipe their wallets if their device is lost or stolen.
8. Simplified Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Many digital wallets allow users to send money instantly to friends or family without the need for bank accounts or cash. This is particularly useful for small, everyday transfers.
9. Environmentally Friendly: As digital wallets reduce the need for physical cards, paper receipts, and other printed materials, they contribute to reducing paper waste and carbon footprints.
Cons of Using Digital Wallets
1. Device Dependency: Digital wallets require smartphones or devices, so if your device is lost, stolen, or damaged, you could lose access to your funds until the issue is resolved.
2. Limited Merchant Acceptance: While digital wallet usage is growing, not all merchants, especially smaller businesses, accept digital wallet payments, which can be frustrating in certain situations.
3. Security Vulnerabilities: Although digital wallets use encryption, they are still susceptible to risks like hacking, malware, and phishing attacks. If a wallet provider’s security is breached, user data could be compromised.
4. Privacy Concerns: Digital wallets collect personal data about your spending habits, location, and more, which can be used for targeted advertising. This raises concerns about data privacy and how it’s handled.
5. Transaction Fees: Some digital wallets charge fees for certain services, such as transferring funds to a bank account or withdrawing cash. These charges can add up over time for frequent users.
Having weighed the advantages against the potential drawbacks, it becomes clear that digital wallets represent more than just a technological upgrade. For those ready to adopt this digital transformation, platforms like Pocketly are leading the charge by combining wallet convenience with innovative lending solutions.
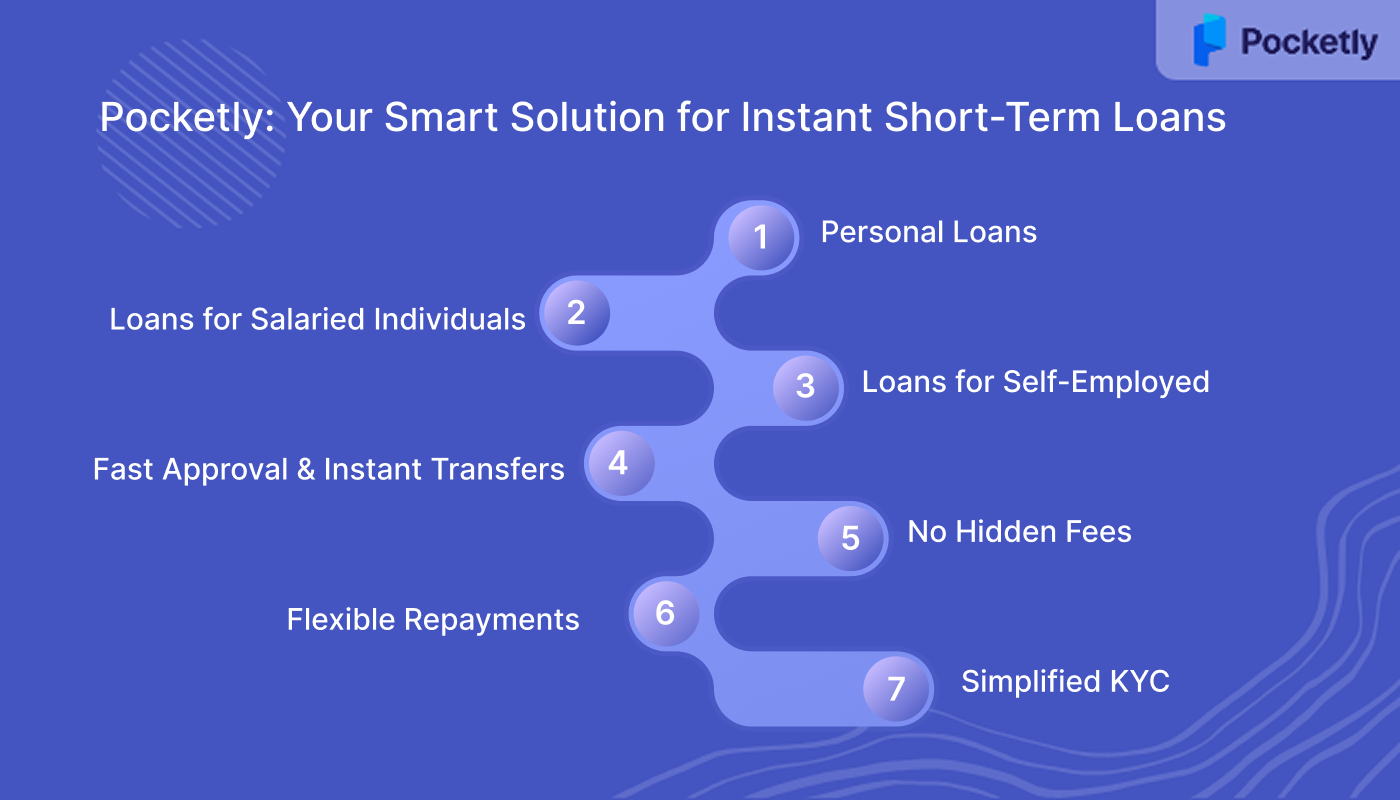
Pocketly: Your Smart Solution for Instant Short-Term Loans
Pocketly is a digital lending platform dedicated to helping young Indians manage their financial needs with ease and transparency. Offering quick, hassle-free loans, Pocketly is your go-to solution for managing emergencies and short-term cash shortages.
- Personal Loans: Ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000, with flexible EMIs and no collateral required.
- Loans for Salaried Individuals: Tailored to help professionals tackle month-end shortages with quick approval and minimal documentation.
- Loans for Self-Employed: Custom loan options to meet the financial needs of freelancers and entrepreneurs.
- Fast Approval & Instant Transfers: Apply and receive your funds instantly, directly in your bank account.
- No Hidden Fees: Transparent interest rates starting from 2% per month, with processing fees between 1-8% of the loan amount.
- Flexible Repayments: Partial repayments and loan closure at any time, giving you full control of your finances.
- Simplified KYC: Complete your loan application with ease through a minimal, paperless KYC process.
Conclusion
In this blog, we’ve explored the ins and outs of digital wallets, what they are, how they work, and their key advantages and drawbacks. Digital wallets offer unmatched convenience, security, and efficiency in managing daily transactions, tracking spending, and accessing financial services. However, like any tool, they come with their own set of challenges, such as device dependency and privacy concerns.
If you're looking for a flexible and secure way to manage your finances, Pocketly offers a seamless digital lending platform to meet your financial needs. With quick access to short-term loans, flexible repayment options, and no collateral required, download now on iOS or Android today!
FAQs
1. Can the money be withdrawn from my digital wallet?
Yes, you can withdraw money from most digital wallets by transferring funds to your linked bank account. Some wallets also offer cash withdrawal at ATMs, depending on the service provider.
2. How do I find my digital wallet card number?
Your digital wallet card number is typically visible in the wallet’s settings under the “Cards” section. If you are using a virtual card, it may be available in the wallet app or through the service’s online platform.
3. Which is the most used digital wallet in India?
Paytm is one of the most widely used digital wallets in India, with millions of users for both online and offline payments, bill payments, and recharges.
4. Which digital wallet has no KYC in India?
Some digital wallets allow limited transactions without full KYC, such as MobiKwik or FreeCharge, but for higher transaction limits and full access, KYC verification is usually required.
5. Does Paytm wallet charge money?
Paytm does not charge fees for most transactions, like money transfers, recharges, and bill payments. However, charges may apply for certain services like wallet-to-bank transfers or merchant payments.