As you begin your career, one thing becomes clear: your ability to manage money can have a significant impact on your professional journey. According to a recent survey by the National Financial Educators Council, employers now consider financial literacy an important factor when hiring for entry-level roles.
In today’s job market, employers are looking for more than just qualifications. They value candidates who can handle financial responsibilities and demonstrate an understanding of financial principles. Mastering these skills doesn’t just help you manage your finances better but can also help you stand out in a competitive job market and prepare you for long-term success.
In this blog, we will explore the key financial skills that employers value, helping you take practical steps toward building a strong career foundation.
Key Takeaways
- Hard Financial Skills Are Essential: Skills like financial analysis, budgeting, and financial reporting are foundational for roles in accounting, financial planning, and management.
- Soft Financial Skills Matter Too: Communication, problem-solving, and ethical decision-making are highly valued for their role in driving successful financial strategies and team collaboration.
- Digital and Analytical Proficiency is Key: Mastery of tools like Excel, Power BI, and financial software is essential for handling complex data, forecasting, and decision-making.
- Continuous Learning is Crucial: Building and improving financial skills involves self-assessment, professional certifications, and practical application in both personal and professional settings.
What are Financial Skills?
Financial skills encompass both hard and soft competencies required to manage and assess money effectively. Hard skills refer to technical abilities such as budgeting, financial analysis, and reporting, while soft skills include decision-making, strategic thinking, and financial communication. Both types of skills are critical for professionals at all levels, from individuals managing personal finances to executives making strategic decisions.
In various financial roles, these skills are crucial:
- Accountants need strong technical skills like bookkeeping, taxation knowledge, and financial reporting for accurate record-keeping and compliance.
- Financial Analysts rely on analysing financial data, assessing market trends, and forecasting future growth or risks to guide investment and business decisions.
- CFOs (Chief Financial Officers) must possess technical and soft skills, such as leadership, strategic decision-making, and communication of complex financial information to stakeholders.
Financial skills are integral to the success and stability of any organisation. These skills help businesses in resource allocation, investment strategies, and risk management.
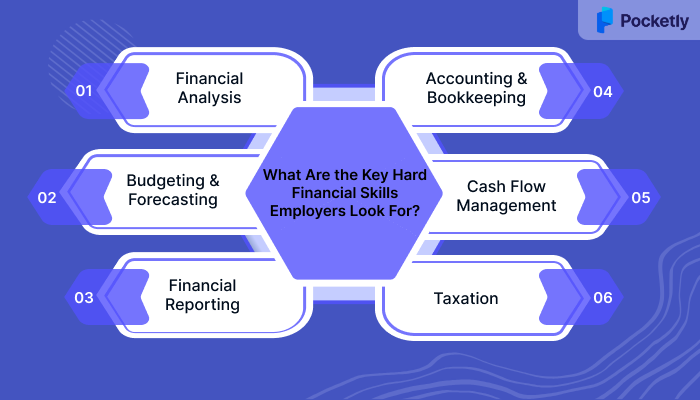
What Are the Key Hard Financial Skills Employers Look For?
Hard financial skills are the technical abilities needed to manage financial operations. These skills are essential for roles in accounting, financial analysis, and corporate finance. Below are some of the most valuable hard financial skills:
1. Financial Analysis
Financial analysis involves examining and interpreting financial data to evaluate an organisation's performance and financial health. This includes analysing balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements, and profitability ratios to understand trends, assess risks, and make projections.
Key Focus Areas:
- Analysing financial ratios like return on equity, profit margins, and current ratios
- Identifying patterns in financial performance and market trends
- Supporting financial forecasting and investment decisions
2. Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting are processes where financial professionals predict future revenues, expenses, and capital needs. This involves creating detailed budgets, adjusting forecasts based on actual performance, and ensuring funds are allocated efficiently.
Key Focus Areas:
- Creating annual budgets and cash flow projections
- Monitoring actual performance against budgeted figures
- Adjusting forecasts to reflect business changes or economic conditions
3. Financial Reporting
Financial reporting refers to the creation of financial statements that provide a clear view of a company’s financial status. Professionals use frameworks like GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) or IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) to prepare reports such as income and cash flow statements and balance sheets.
Key Focus Areas:
- Preparing statements that comply with accounting standards
- Ensuring accurate classification of financial transactions
- Presenting financial reports to stakeholders like investors or regulatory bodies
4. Accounting and Bookkeeping
Accounting and bookkeeping involve recording and tracking financial transactions. This includes maintaining ledgers, reconciling bank statements, and ensuring accurate documentation of financial data. These tasks are critical for preparing financial reports and ensuring tax compliance.
Key Focus Areas:
- Recording daily financial transactions using accounting software (QuickBooks, Xero)
- Managing general ledgers and preparing trial balances
- Handling accounts receivable and accounts payable
5. Cash Flow Management
Cash flow management involves monitoring the inflows and outflows of cash to ensure that an organisation has enough liquidity to meet its obligations. It requires tracking day-to-day transactions and ensuring that cash is available for operational expenses, investments, and debt repayments.
Key Focus Areas:
- Monitoring cash flow projections and actual cash positions
- Managing working capital to ensure enough liquidity for operations
- Implementing strategies to manage cash shortages or surpluses
6. Taxation
Taxation skills involve understanding and applying tax laws and regulations to minimise liabilities and ensure compliance. Financial professionals with expertise in taxation help organisations and individuals plan for tax payments, claim deductions, and avoid penalties.
Key Focus Areas:
- Preparation and tax return filing for individuals or businesses
- Understanding corporate, sales, and personal tax laws
- Identifying tax-saving opportunities and complying with tax regulations
Technical expertise alone rarely determines professional success; there are human-centered skills that often distinguish exceptional financial professionals from their technically competent peers.
What Are the Important Soft Financial Skills Employers Look For?
Soft financial skills are essential for professionals as they complement technical financial abilities, allowing individuals to manage complex situations, manage relationships, and drive organisational success. Here are the key soft financial skills that employers highly value:
1. Communication Skills
The ability to communicate financial concepts clearly and concisely is essential, especially when dealing with non-financial stakeholders. Being able to explain complex financial information in a simple manner is important for influencing decisions.
Key Focus Areas:
- Explaining financial data to non-financial teams
- Writing clear financial reports and presentations
- Effectively discussing financial strategies with senior management
2. Problem-Solving
Financial professionals are often required to address challenges such as budget deficits, cost overruns, or financial inefficiencies. Problem-solving skills enable you to identify solutions to complex financial issues and implement effective strategies.
Key Focus Areas:
- Identifying and analysing financial problems
- Creating actionable solutions that minimise financial risk
- Working with cross-functional teams to resolve financial obstacles
3. Time Management
Financial professionals often juggle multiple projects with tight deadlines. Efficiently managing time, prioritising tasks, and meeting deadlines ensures that key financial activities like reporting, audits, or budget planning are completed on time.
Key Focus Areas:
- Prioritising urgent financial tasks
- Managing multiple deadlines effectively
- Organising daily workloads to ensure maximum efficiency
4. Decision Making
In finance, professionals often have to make decisions that will impact the company’s financial health, investments, and long-term strategy. Whether it's determining the best course of action during a financial crisis or evaluating which investments to prioritise, strong decision-making skills allow professionals to assess risks, understand market trends, and make informed choices.
Key Focus Areas:
- Evaluating financial data
- Weighing risks and benefits
- Making decisions quickly, even under pressure
5. Ethics
Finance is particularly sensitive when it comes to ethical considerations due to the handling of financial data, investments, and company funds. Ethics in finance ensures trust, credibility, and compliance with legal and regulatory standards. Professionals who are ethically driven maintain transparency, prevent fraudulent activities, and promote financial integrity.
Key Focus Areas:
- Ensuring compliance with financial regulations
- Upholding honesty in financial reporting
- Avoiding conflicts of interest and unethical practices
Organisations increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, requiring professionals who can adopt sophisticated analytical tools with confidence. This technological shift has elevated digital proficiency from a nice-to-have skill to an essential requirement.
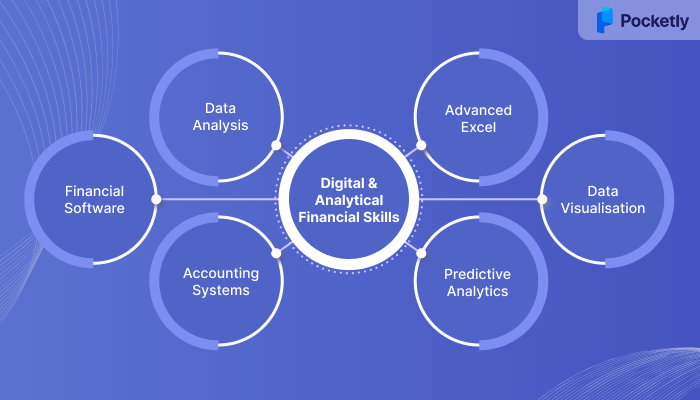
What are the Digital and Analytical Financial Proficiency Skills Employers Look For?
Employers these days are looking for professionals who can leverage technology and data analytics to develop financial strategies. These digital and analytical skills are essential for working with large datasets, using financial software, and understanding key financial metrics. Below are some of the proficiency skills employers highly value:
1. Data Analysis and Financial Modelling
Financial professionals need to analyse large volumes of data and build financial models to forecast performance, identify trends, and support business decisions. This includes using Excel, Power BI, or other data tools to create comprehensive financial models.
Key Focus Areas:
- Analysing historical financial data for forecasting
- Creating dynamic financial models for budgeting and valuation
- Using tools like Excel, R, or Python for complex financial calculations
2. Financial Software Proficiency
Being proficient in financial software is essential for managing daily financial tasks, from accounting to reporting. Familiarity with tools such as SAP, Oracle Financial Services, or QuickBooks is highly sought after by employers.
Key Focus Areas:
- Managing financial transactions and reports using software
- Tracking and reconciling accounts through automated systems
- Generating financial statements, tax returns, and audit reports
3. Accounting Software and ERP Systems
Knowledge of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems helps streamline financial operations across the organisation. Tools like SAP, NetSuite, or Microsoft Dynamics are used to manage financial data and integrate it with other business functions.
Key Focus Areas:
- Managing financial records across multiple departments
- Automating processes like invoicing, procurement, and financial reporting
- Maintaining up-to-date compliance with accounting standards and regulations
4. Advanced Excel Skills
Excel is the most powerful tool for financial analysis, offering a wide range of functions such as pivot tables, VLOOKUP, and complex formulas. Advanced Excel skills are critical for creating financial reports, performing calculations, and analysing trends.
Key Focus Areas:
- Using complex formulas, data models, and pivot tables
- Automating data analysis and report generation
- Conducting sensitivity analysis and scenario planning
5. Data Visualisation and Reporting Tools
Data visualisation tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Google Data Studio are essential for presenting complex financial data in a clear, visual format. These tools help stakeholders easily understand trends and make data-driven decisions.
Key Focus Areas:
- Designing dashboards for key financial metrics
- Communicating complex data in visual formats for executive decision-making
- Creating automated reports and visual representations of financial performance
6. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics involves using historical financial data to make predictions about future trends. Understanding machine learning techniques and predictive analytics tools helps financial professionals forecast future revenue, expenses, or market changes.
Key Focus Areas:
- Using statistical models and machine learning for predictions
- Analysing financial patterns and preparing forecasts
- Employing data science techniques to assess financial risks
Becoming financially proficient requires careful planning, structured learning, and consistent application. It involves a mix of formal education, practical experience, and ongoing development.
How to Build and Improve Your Financial Skills?
Building and improving financial skills is a continuous process that blends self-assessment, structured learning, and practical application. If you are just starting out, here's how you can develop and strengthen your financial skills:
1. Start with Self-Assessment: Begin by evaluating your understanding of budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management. Identify which areas you’re comfortable with and which require more focus. Regularly self-assess your goals and revisit your skill levels to track improvement and develop new areas.
2. Pursue Professional Certifications: Gaining specialised knowledge and credentials is a great way to build and improve your financial skills. Consider pursuing certifications such as:
- CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst): Focuses on investment analysis, portfolio management, and financial markets.
- CPA (Certified Public Accountant): Ideal for those seeking expertise in accounting, taxation, and financial reporting.
- FRM (Financial Risk Manager): For professionals interested in risk management roles, emphasizing risk analysis and mitigation strategies.
- PMP (Project Management Professional): A great option if you're managing financial projects or leading teams with budgetary responsibilities.
3. Utilise Online Learning Platforms: Platforms like Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and Corporate Finance Institute (CFI) are excellent resources for building and improving financial knowledge. Start with beginner-level courses to grasp core concepts, then progressively move to advanced topics that will allow you to deepen your expertise and apply financial concepts directly to real-world scenarios.
4. Practical Application in Personal and Professional Settings: Gaining theoretical knowledge is valuable, but applying these skills in real-life scenarios is quintessential to improving your financial competence.
- Personal Finance: Start by managing your own budget, saving for short and long-term goals, and also investing in assets like mutual funds or stocks.
- Professional Application: Apply finance skills at work by managing projects within budgets, using financial reporting tools, analysing financial statements, and contributing to financial planning and cost control.
- Simulations and Case Studies: Participate in financial planning workshops or simulations to practice real-world scenarios. Many online platforms offer free or low-cost resources for such exercises.
5. Stay Updated with Industry Trends: Keep yourself abreast with the latest financial news, blogs, and research reports from trusted sources such as The Wall Street Journal, Investopedia, or Bloomberg. Also, participate in webinars, attend industry conferences, and read financial books to broaden your understanding.
For students and young professionals building their expertise, access to flexible financial tools can provide valuable hands-on experience with loan management and repayment planning.
Why Pocketly is the Financial Solution You Need
For students and professionals looking to take control of their financial journey, Pocketly offers a flexible and accessible solution. With loan amounts ranging from ₹1,000 to ₹25,000, Pocketly provides instant personal loans with affordable interest rates starting at just 2% per month and processing fees between 1-8%. Whether you need quick funds for educational expenses or managing unexpected costs, Pocketly makes the loan process smooth with flexible EMI options and no hidden charges.
Conclusion
Financial skills are essential for both personal growth and career advancement. From mastering budgeting and financial reporting to enhancing decision-making and risk management abilities, these skills enable professionals to manage their finances and be instrumental in business success.
Whether you're starting out in your career or looking to refine your financial expertise, developing these skills will make you an irreplaceable asset the employers and set you on the path to financial independence.
For those looking to manage unexpected expenses or take control of their financial journey, Pocketly offers an easy, fast, and transparent way to access loans. As a digital lending platform, it ensures a seamless borrowing experience without the hassle. Download Pocketly now on iOS or Android to get started.
FAQs
1. What are the 4 A's of financial management?
The 4 A’s of financial management are Accounting, Analysis, Allocating (resources), and Assessing. These components ensure efficient management of finances by tracking, analyzing, distributing resources, and evaluating financial outcomes.
2. How to boost a finance resume?
To boost your finance resume, highlight certifications (CFA, CPA), financial software skills, and quantifiable achievements in previous roles. Tailor your resume to showcase your experience in budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting to align with the job requirements.
3. What are the 5 C's of financial management?
The 5 C’s of financial management include Cash, Cost, Capital, Control, and Communication. They focus on managing liquidity, expenses, securing funding, implementing financial controls, and effectively communicating financial strategies.
4. Which field is best in finance?
Fields like investment banking, financial analysis, and corporate finance are considered the best in finance due to high earning potential and career growth opportunities. Specializing in areas like FinTech and financial risk management can also provide lucrative prospects.
5. What qualifications do I need to work in finance?
To work in finance, you typically need a degree in Finance, Accounting, or Economics. Advanced certifications like CFA, MBA in Finance, or CPA can significantly boost your career prospects in the industry.
6. What experience do I need to work in finance?
For entry-level positions, internships, or experience in accounting, budgeting, or financial analysis is sufficient. For more senior roles, experience in financial forecasting, project management, and leadership positions is required to show expertise and strategic decision-making ability.