Financial education isn’t something that simply appears when you need it most; it’s a process that shapes how we handle money, make choices, and pursue long-term goals. The gap in knowledge can often be the difference between flourishing and merely getting by.
From understanding the basics of budgeting to grasping the ins and outs of investments, having a solid grasp of financial principles empowers us to take control of our financial futures.
It's not about mastering every detail at once, but gaining enough understanding to avoid mistakes, make better choices, and ultimately build wealth. The earlier you begin, the more prepared you'll be to make money work for you, instead of the other way around.
In this blog, we’ll explore why financial education is essential, the benefits, and the key concepts you need to start building a strong financial foundation.
Key Takeaways
- Financial Education is Essential: It forms the foundation for effective personal financial management, helping individuals make smarter decisions about budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management.
- Benefits Extend Beyond Basic Money Management: Financial literacy leads to better credit scores, increased savings, reduced financial stress, and the ability to make informed investment choices.
- Addressing Gaps in Financial Education: Many communities, especially low-income and minority groups, lack access to financial education. Expanding access to financial resources is key to reducing inequalities.
- Building Financial Goals and Planning: Financial education helps individuals set clear, achievable goals and create structured plans to reach them, leading to long-term financial security.
- The Role of Financial Education in Debt and Savings: Financially educated individuals are better equipped to manage debt, avoid high-interest traps, and build emergency savings to face unexpected challenges.
What is Financial Education?
Financial education is the understanding of how money works and how to manage it effectively. It includes learning how to budget, save, invest, and plan for the future. With financial education, you can make better choices about managing your money, ensuring you can cover expenses, save for goals, grow your wealth, and prepare for emergencies.
Budgeting helps you control your spending, saving builds your financial security, investing grows your wealth over time, and financial planning gives you a roadmap to reach your financial goals. Ultimately, the importance of financial education is that it provides the knowledge and tools needed to build a stable financial future and avoid common money mistakes.
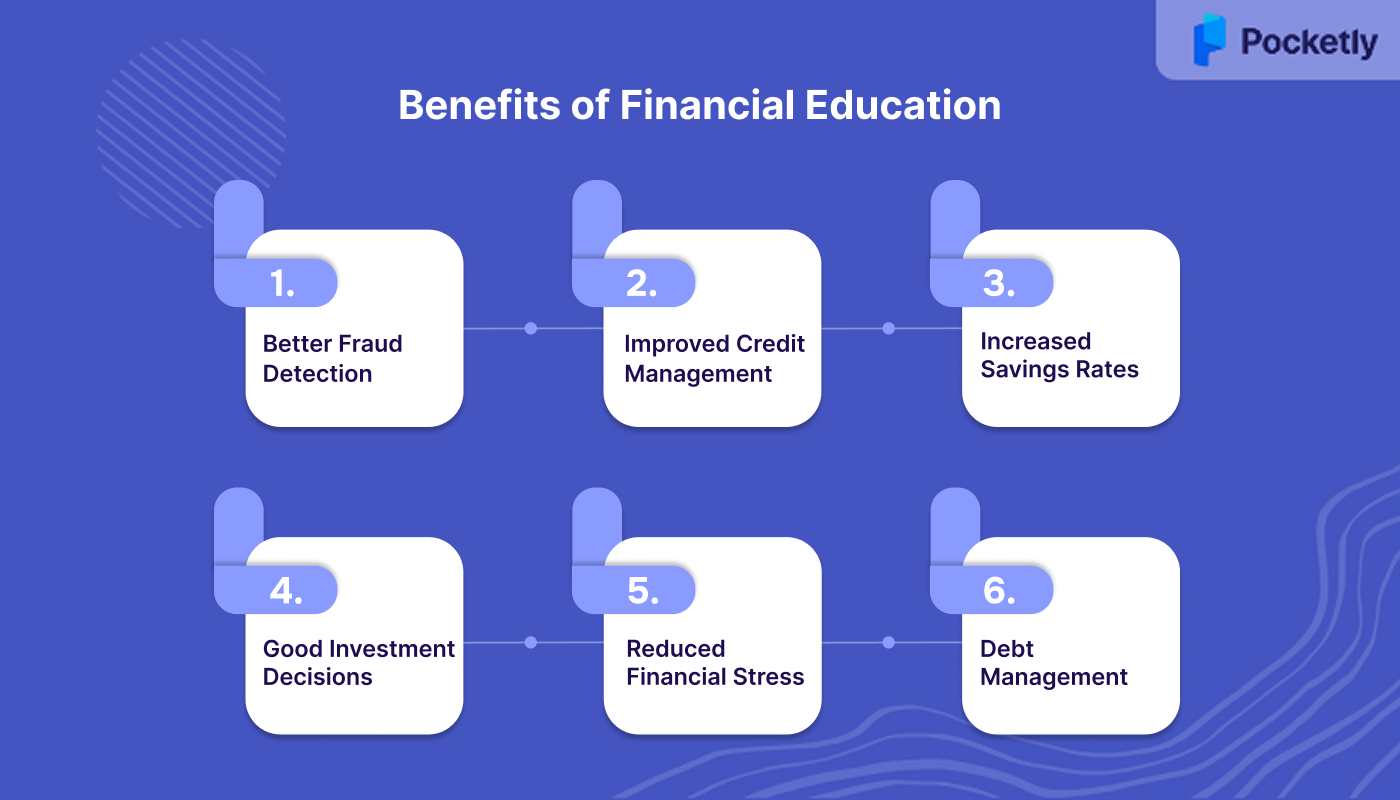
Benefits of Financial Education
Financial education goes beyond basic money management. It equips individuals with the knowledge to make sound credit, savings, and investment choices. Studies show that financially literate people are less likely to fall into high-interest debt and better at spotting fraud.
Let’s explore some key benefits in detail:
- Better Fraud Detection: Financially knowledgeable individuals are more adept at spotting scams. A study found that those with higher financial literacy were 36% more likely to detect fraud compared to those with lower literacy levels .
- Improved Credit Management: Understanding credit helps in maintaining a good credit score. For instance, individuals with financial literacy are less likely to carry high-interest credit card debt, leading to better credit profiles.
- Increased Savings Rates: Financial education encourages saving. Research indicates that individuals with financial literacy are more likely to have emergency savings, providing a safety net during unexpected financial challenges.
- Good Investment Decisions: Knowledge of financial principles leads to more informed investment choices. Studies show that financially educated individuals are more likely to invest in the stock market, thus increasing wealth over time.
- Reduced Financial Stress: Understanding money management reduces anxiety. Financially literate individuals often experience less stress related to money, as they are better equipped to handle financial decisions and challenges.
- Debt Management: Understanding how debt works allows you to manage existing debt effectively, avoid high-interest traps, and plan a strategy for paying it off.
These benefits are only half the story; the true power lies in how this knowledge translates into practical, day-to-day money management.
The Role of Financial Education in Personal Financial Management
Financial education plays a critical role in personal financial management by providing individuals with the knowledge and tools needed to manage their money and plan for the future. Here’s how financial education impacts personal financial management:
1. Budgeting and Expense Tracking
At the core of personal financial management is budgeting. Financial education teaches you how to track income and expenses, allocate funds to different categories, and ensure you're not spending more than you earn. Without financial education, it’s easy to overlook small but frequent expenses, leading to poor financial decisions.
By learning how to budget, you can:
- Plan for essential needs, such as housing, food, and transportation.
- Set aside money for savings and investments.
- Identify areas where you can cut back on non-essential spending.
- Build a cushion for emergencies or unexpected expenses.
Studies have shown that people who track their spending and stick to a budget are more likely to save money and avoid debt.
2. Debt Management
Understanding how to manage debt is another key component of financial education. Financially educated individuals are better equipped to use debt strategically, whether it’s a mortgage, car loan, or credit card debt. They know the difference between "good debt" (debt that helps increase net worth, like a home loan) and "bad debt" (debt with high interest and no return on investment, like credit card balances).
With financial education, individuals can:
- Avoid accumulating high-interest debt by understanding credit cards, loans, and interest rates.
- Prioritise paying off high-interest debts first to reduce the total amount paid over time.
- Learn how to use credit responsibly, including when to open a new credit line or take on debt.
- Understand the debt-to-income ratio and its impact on borrowing power.
Managing debt responsibly can prevent the snowballing of interest and fees, improve credit scores, and lead to greater financial freedom.
3. Saving and Emergency Funds
One of the most important aspects of financial education is learning how to save. Without a solid understanding of the importance of saving, many individuals fail to set aside money for emergencies, retirement, or major life goals. Financial education teaches building emergency funds to cover unexpected expenses, providing financial security during job loss, medical emergencies, or unexpected bills.
A solid savings strategy includes:
- Setting up automatic transfers to savings accounts.
- Understanding the importance of an emergency fund that covers at least 3-6 months of living expenses.
- Investing for long-term goals, such as retirement, through vehicles like 401(k)s, IRAs, or mutual funds.
According to various surveys, financially educated individuals are more likely to have emergency savings and less likely to rely on credit to cover unplanned expenses.
4. Investing and Wealth Building
Financial education is crucial for understanding how investing works and how to grow wealth over time. Learning about the different types of investments, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and real estate, allows individuals to learn where to allocate their money for long-term growth. Without this knowledge, people are often hesitant to invest, leaving them reliant on traditional savings accounts with low returns.
With financial education, individuals can:
- Learn how to invest in diversified portfolios that match their risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Understand compound interest and how it can help grow wealth over time.
- Make informed decisions about retirement savings, including contributing to employer-sponsored retirement plans and individual retirement accounts (IRAs).
- Take advantage of tax-advantaged savings and investment opportunities.
Investing is a long-term strategy, and financial education gives individuals the confidence and knowledge to start building wealth, even with modest amounts of money.
5. Financial Goal Setting and Planning
A major benefit of financial education is its focus on setting realistic financial goals. Whether it’s buying a home, paying off debt, or saving for retirement, financial education teaches individuals how to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. This helps individuals stay on track and motivated as they work towards their financial aspirations.
Through goal setting, individuals can:
- Identify short-term and long-term financial goals.
- Break down goals into manageable steps, such as saving a specific amount each month.
- Track progress and adjust plans as needed to stay on course.
Without financial education, goal setting may lack structure and lead to discouragement. Financial education ensures that goals are not only set but also achievable.
6. Tax Planning and Minimising Liabilities
Understanding taxes and tax strategies is another critical component of financial education. Tax planning can help individuals minimise their tax liabilities and increase savings. This knowledge is especially important for individuals with investments, self-employed people, or those with complex financial situations.
Financial education enables individuals to:
- Understand tax brackets, deductions, credits, and exemptions.
- Learn about tax-efficient investing and retirement planning to minimise tax burdens.
- Plan for significant tax events, such as capital gains, inheritance taxes, or self-employment taxes.
Without knowledge of tax rules, individuals may miss out on opportunities to reduce their tax bills or might face penalties for underpaying taxes.
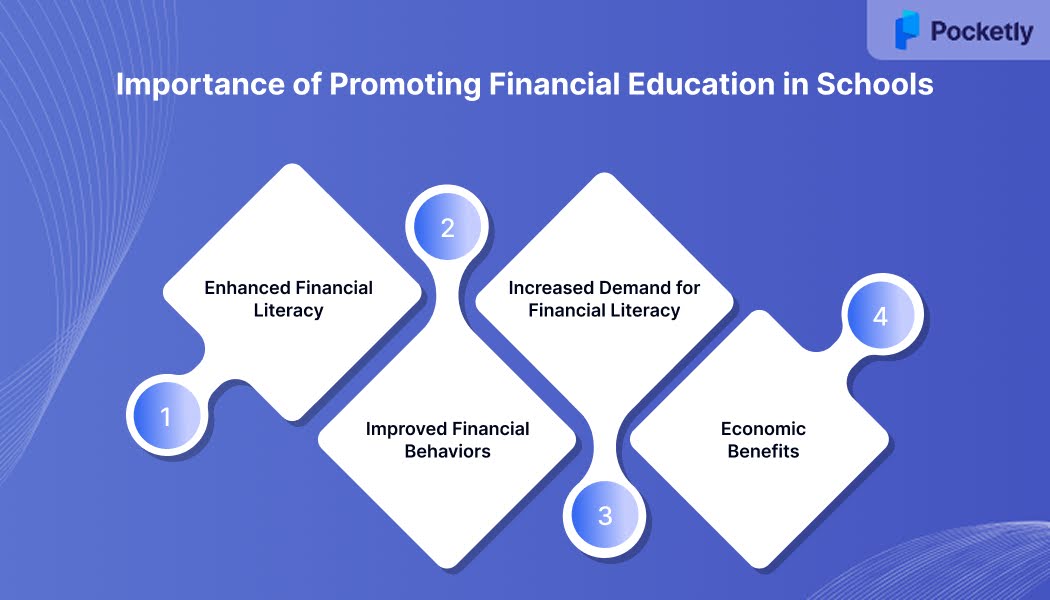
The Importance of Promoting Financial Education in Schools
Integrating financial education into school curricula is crucial for equipping students with the skills required to overcome the complexities of personal finance. Beyond basic budgeting, it is also important to understand credit, managing debt, and saving for future goals. Here's why it's imperative:
- Enhanced Financial Literacy: Studies indicate that students who receive financial education are more likely to understand concepts like credit scores, interest rates, and budgeting. For instance, a study in Georgia and Texas found that students who received personal finance instruction had higher credit scores and were less likely to be delinquent on credit card payments.
- Improved Financial Behaviors: Financial education fosters positive financial habits. Research shows that individuals who have received financial education tend to save more, invest wisely, and manage debt effectively, leading to greater financial stability in adulthood .
- Increased Demand for Financial Literacy: There's a growing consensus on the need for financial education. A survey revealed that 83% of U.S. adults believe personal finance should be a high school graduation requirement, and 82% wish they had received such education during their schooling .
- Economic Benefits: Financially literate individuals contribute to the economy by making informed spending, saving, and investing decisions. This leads to a more stable financial system and reduced reliance on social welfare programs.
Despite the clear benefits of early financial education, the reality is that many individuals enter adulthood without these essential skills. The absence of comprehensive financial education creates a cascade of challenges that can persist for decades.
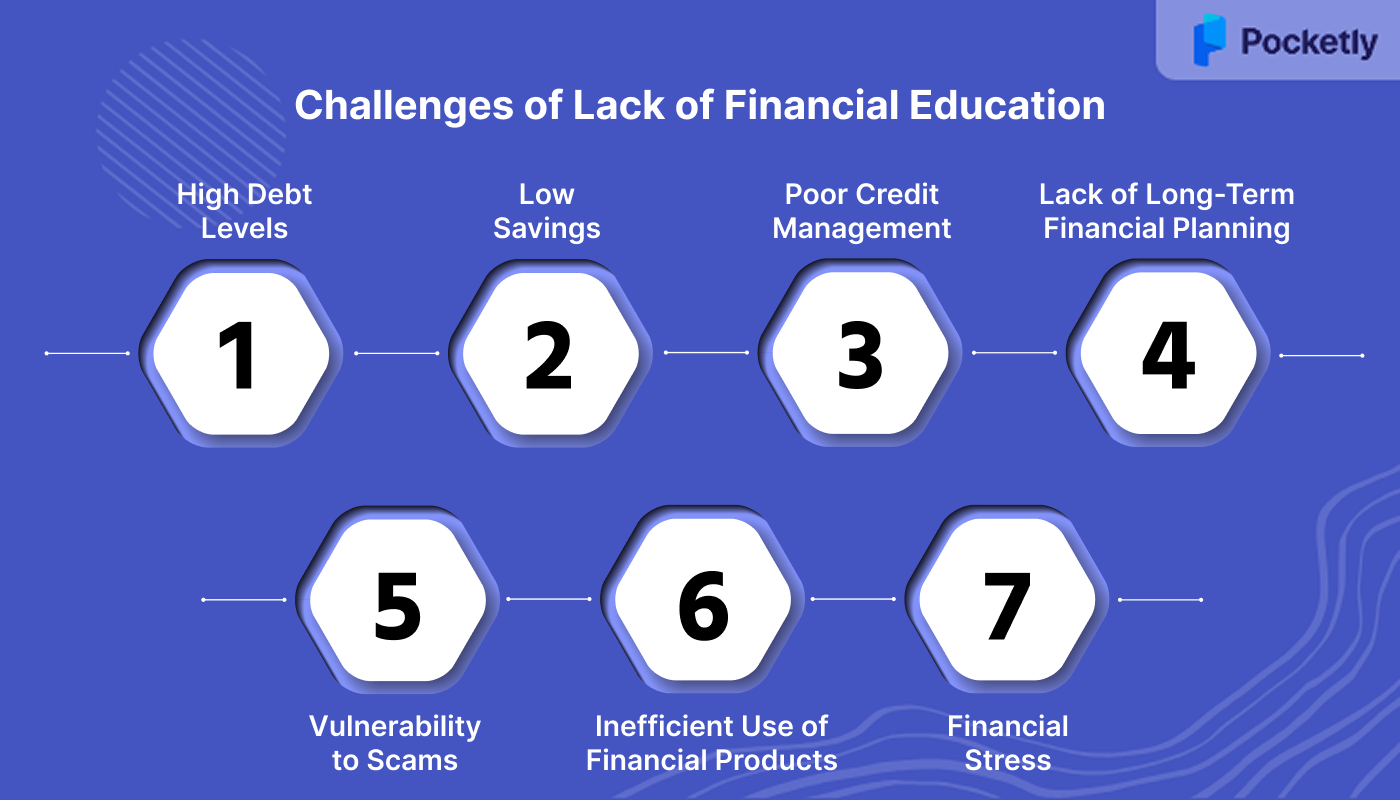
Challenges of Lack of Financial Education
The lack of financial education creates barriers to managing money effectively, leading to poor decisions, financial instability, and long-term challenges. Without knowledge of key financial concepts like budgeting, saving, and managing debt, people often face high levels of debt, low savings, and poor credit scores.
Here are the key challenges caused by the lack of financial education:
- High Debt Levels: Without understanding credit, individuals may accumulate high-interest debt, which becomes difficult to repay, leading to long-term financial struggles.
- Low Savings: Lack of financial education often results in poor saving habits, leaving individuals unprepared for emergencies or unexpected expenses.
- Poor Credit Management: Without knowledge of credit, individuals may miss payments or accumulate debt, damaging their credit scores and limiting future borrowing options.
- Lack of Long-Term Financial Planning: Without education, setting and achieving long-term financial goals like saving for retirement or buying a home becomes difficult.
- Vulnerability to Scams: Individuals with limited financial education are more susceptible to scams or predatory lending due to a lack of understanding of financial products.
- Inefficient Use of Financial Products: Without proper knowledge, individuals may misuse financial products like credit cards or loans, leading to higher fees or missed opportunities.
- Financial Stress: Poor financial management and lack of knowledge often lead to stress, negatively affecting both financial and mental well-being.
Building these skills requires a strategic approach that combines practical habits with ongoing education. The key is knowing where to focus your efforts for maximum impact.
Tips on Improving Financial Literacy
Improving financial literacy is crucial for making informed decisions about money management, building wealth, and ensuring financial security. By gaining a solid understanding of financial principles, individuals can avoid common money mistakes and make smarter investments.
Here are some tips to help improve your financial literacy:
- Track your spending and use budgeting apps to monitor expenses.
- Set clear short-term and long-term financial goals.
- Understand credit, including credit scores and reports.
- Build an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Learn about different investment options and risk management.
- Consult financial advisors or attend workshops for deeper knowledge.
- Pay off high-interest debts first and manage your overall debt.
- Utilize educational resources like books, courses, and workshops.
- Engage in community initiatives and educational programs for hands-on experience.
- Continuously use online learning platforms for self-study and updates.
While individual effort plays a crucial role in building financial literacy, we cannot ignore the broader systemic barriers that prevent entire communities from accessing these opportunities. Financial education isn't just about personal responsibility; it's about ensuring equal access to the tools and knowledge that create financial stability.
Addressing Financial Inequalities and Promoting Equity
To create a more equitable society, it’s essential to address the financial inequalities that exist across different communities. These disparities, often fueled by unequal access to resources and education, disproportionately affect low-income and minority groups.
1. Improving Access to Financial Education Across Different Communities
A major step in addressing financial inequalities is expanding access to financial education, especially in underserved communities. Many individuals, particularly from low-income or minority backgrounds, do not have access to the same financial resources or education as others. In fact, only a small percentage of states require personal finance courses in schools.
By making financial education a priority in all communities, whether through schools, community centers, or online platforms, we can help individuals learn fundamental money management skills. This ensures that everyone has the knowledge needed to manage income, save for the future, and avoid falling into debt traps.
2. Overcoming Disparities and Instilling Financial Equity
To overcome financial disparities, it’s crucial to create systems that promote financial equity. This involves offering targeted financial programs and policies that address the unique challenges faced by low-income and minority communities.
Financial institutions must also be more inclusive in providing services, ensuring that all groups, regardless of background, can access affordable loans, credit, and savings accounts.
Furthermore, rebuilding trust in financial institutions through transparent practices and community outreach can help ensure that vulnerable populations feel empowered to make financial decisions that align with their long-term goals.
Fostering financial equity ensures that everyone, regardless of their starting point, has the opportunity to build wealth and achieve financial independence.
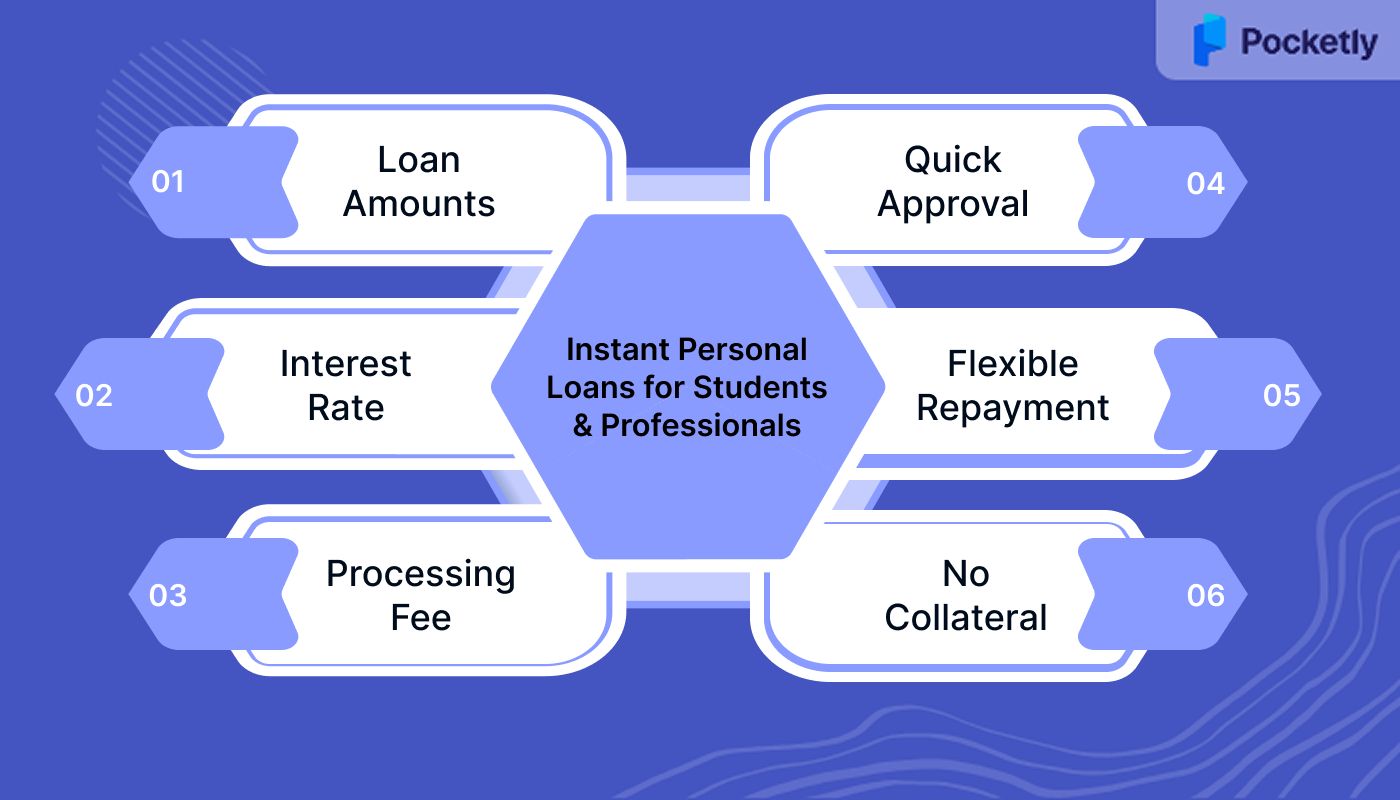
Pocketly: Instant Personal Loans for Students and Professionals
Pocketly is a digital lending platform designed to provide instant personal loans to students and salaried professionals, even without a credit history. The platform offers quick personal loan approvals, minimal documentation, and flexible repayment options.
- Loan Amounts: Borrow between ₹1,000 and ₹25,000 to meet your various financial needs.
- Interest Rate: Enjoy a competitive interest rate of 2% per month, making repayments affordable.
- Processing Fee: Pay a minimal processing fee between 1% to 8% of the loan amount.
- Quick Approval: Get instant loan approval with minimal documentation required.
- Flexible Repayment: Repay your loan through convenient modes like bank transfers, UPI, and digital wallets.
- No Collateral: No need for collateral, get a personal loan based on eligibility and need.
Conclusion
In this blog, we've explored the critical role of financial education in shaping personal financial management and its far-reaching impact on building wealth, managing debt, and preparing for future goals.
Financial education not only empowers individuals to make better decisions but also helps bridge gaps in financial knowledge in underserved communities. By understanding the importance of budgeting, saving, investing, and managing credit, individuals can avoid common financial pitfalls and work towards long-term financial security.
Pocketly offers a simple and effective solution for individuals looking to manage their finances with ease. Download now on iOS or Android to take the first step towards managing your finances and building your credit history!
FAQs
1. What are the 5 principles of financial literacy?
The five key principles of financial literacy are budgeting, saving, managing debt, investing, and planning for retirement. These principles help individuals make informed decisions, control spending, build wealth, and ensure financial stability in the long term.
2. What are the three different types of financial goals?
The three main types of financial goals are short-term goals (e.g., saving for a vacation), medium-term goals (e.g., buying a car or home), and long-term goals (e.g., retirement planning or education savings). Each goal requires different strategies and timelines.
3. What are the subjects of financial education?
Financial education covers a range of subjects, including budgeting, savings, debt management, investing, credit scores, taxes, insurance, retirement planning, and financial decision-making. It equips individuals with the skills to manage their finances effectively.
4. What are the two major types of financial plans?
The two major types of financial plans are personal financial plans, which focus on managing an individual’s finances, and business financial plans, which are designed to guide a company’s financial decisions. Both help achieve financial stability and growth.
5. Which qualification is best for finance?
The best qualifications for a career in finance include a Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in Finance, Accounting, or Economics, along with certifications such as the CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) or CFP (Certified Financial Planner) for specialised expertise. These qualifications enhance career prospects and financial knowledge.